Once the VMware Workstation Pro desktop virtualization software (Type-II hypervisor) is installed on your Ubuntu/Debian system, you must compile the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules for your Ubuntu/Debian system for it to work.
In this article, I will show you how to compile the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules on Ubuntu/Debian. I will also discuss the problems you may face while compiling the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules and how to solve them.
The methods shown in this article should work on the following Linux distributions:
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Linux Mint
- Elementary OS
- Deepin Linux
- KDE Neon
- Other Ubuntu/Debian-based Linux distributions
Table of Contents
- Upgrading Existing Ubuntu/Debian Packages
- Installing Required VMware Kernel Module Build Tools on Ubuntu/Debian
- Disabling UEFI Secure Boot from the BIOS/UEFI Firmware of Your Motherboard
- Method 1: Compiling the Official VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules on Ubuntu/Debian
- Method 2: Downloading and Compiling Patched VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules on Ubuntu/Debian
- Fixing VMware Workstation Pro Services Fail to Start on Ubuntu/Debian
- Conclusion
- References
Upgrading Existing Ubuntu/Debian Packages
Before attempting to compile VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules, you should install all the available updates on your Ubuntu/Debian system.
To check if new updates are available on your Ubuntu/Debian system, run the following command:
$ sudo apt update
If any updates are available for your Ubuntu/Debian system, you will see them in the output of the command.
As you can see, 28 packages can be upgraded on my Ubuntu/Debian system.

To install all the available updates on your Ubuntu/Debian system, run the following command:
$ sudo apt full-upgrade
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press .
The updates are being downloaded and installed. It will take a while to complete.

At this point, all the updates should be installed on your Ubuntu/Debian system.
For the changes to take effect, reboot your Ubuntu/Debian system.
$ sudo reboot
Installing Required VMware Kernel Module Build Tools on Ubuntu/Debian
To install the required tools for building the VMware Kernel Modules on Ubuntu/Debian, run the following command:
$ sudo apt install build-essential linux-headers-$(uname -r) git
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press .
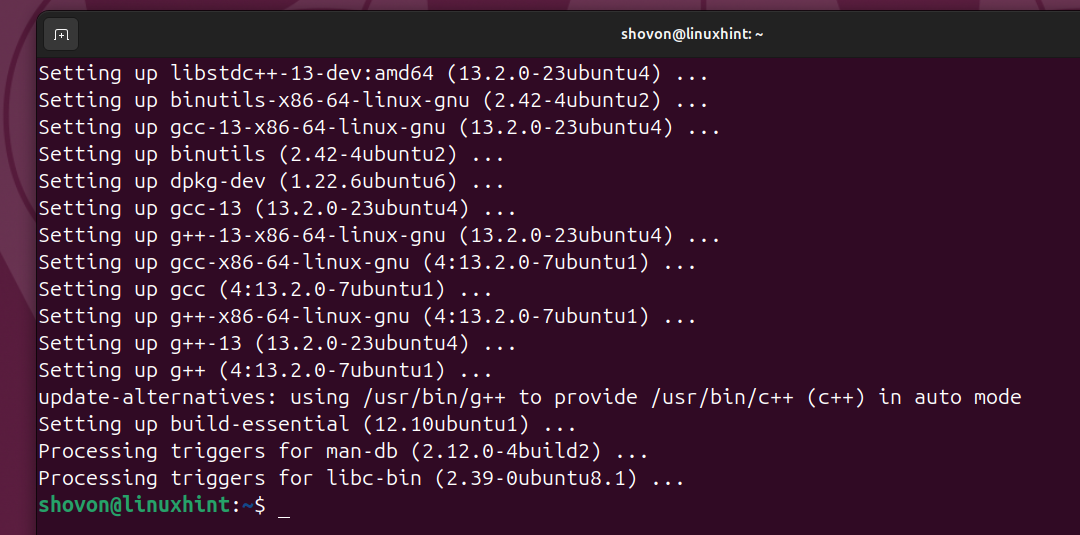
All the required packages are being downloaded and installed. It will take a while to complete.
At this point, all the required build tools should be installed.
Disabling UEFI Secure Boot from the BIOS/UEFI Firmware of Your Motherboard
By default, VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules won’t load at boot time if UEFI Secure Boot is enabled in the BIOS/UEFI Firmware of your motherboard.
To load VMware Workstation Pro kernel module at boot time and use VMware Workstation Pro, you must disable UEFI Secure Boot from the BIOS/UEFI firmware of your motherboard.
If you want to load the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules without disabling UEFI Secure Boot, you must sign the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules after they are compiled and installed on your Ubuntu/Debian system.
Method 1: Compiling the Official VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules on Ubuntu/Debian
The official VMware Kernel Modules (installed alongside the VMware Workstation Pro installation) should compile on most Ubuntu/Debian versions and Ubuntu/Debian-based Linux distributions just fine.
To compile the official VMware Kernel Modules on Ubuntu/Debian, run the following command:
$ sudo vmware-modconfig --console --install-all
The latest version of the VMware Workstation Pro (v17.5.2) kernel modules won’t compile on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS at the time of this writing.
If you attempt to compile the VMware Workstation Pro v17.5.2 on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, you might see the following error messages. The problem is that the VMware Workstation Pro v17.5.2 kernel modules does not support latest Linux kernels yet. So, it fails to compile.
To solve this problem, you must compile the patched version of the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules.

Here is the full error message.
[AppLoader] Use shipped Linux kernel AIO access library.
An up-to-date "libaio" or "libaio1" package from your system is preferred.
[AppLoader] GLib does not have GSettings support.
Stopping VMware services:
VMware Authentication Daemon done
Virtual machine monitor done
make: Entering directory '/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only'
Using kernel build system.
/usr/bin/make -C /lib/modules/6.8.0-31-generic/build/include/.. M=$PWD SRCROOT=$PWD/. \
MODULEBUILDDIR= modules
make[1]: Entering directory '/usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic'
warning: the compiler differs from the one used to build the kernel
The kernel was built by: x86_64-linux-gnu-gcc-13 (Ubuntu 13.2.0-23ubuntu4) 13.2.0
You are using: gcc (Ubuntu 13.2.0-23ubuntu4) 13.2.0
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/driver.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/driverLog.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/hostif.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/apic.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/comport.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/cpuid.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/crosspage.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/memtrack.o
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/crosspage.o: warning: objtool: CrossPage_CodePage+0x207: 'naked' return found in RETHUNK build
make[3]: *** [scripts/Makefile.build:243: /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/crosspage.o] Error 255
make[3]: *** Deleting file '/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/common/crosspage.o'
make[3]: *** Waiting for unfinished jobs....
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/hostif.c:2926:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018HostIFCheckTrackedMPN\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
2926 | HostIFCheckTrackedMPN(VMDriver *vm, // IN: The VM instance
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/hostif.c:3046:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018HostIFWritePhysicalWork\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
3046 | HostIFWritePhysicalWork(MA ma, // MA to be written to
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/hostif.c:3205:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018HostIFStartTimer\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
3205 | HostIFStartTimer(Bool rateChanged, //IN: Did rate change?
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/driver.c:271:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018LinuxDriverInit\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
271 | LinuxDriverInit(void)
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only/linux/driver.c:339:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018LinuxDriverExit\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
339 | LinuxDriverExit(void)
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
make[2]: *** [/usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic/Makefile:1926: /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only] Error 2
make[1]: *** [Makefile:240: __sub-make] Error 2
make[1]: Leaving directory '/usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic'
make: *** [Makefile:117: vmmon.ko] Error 2
make: Leaving directory '/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmmon-only'
make: Entering directory '/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only'
Using kernel build system.
/usr/bin/make -C /lib/modules/6.8.0-31-generic/build/include/.. M=$PWD SRCROOT=$PWD/. \
MODULEBUILDDIR= modules
make[1]: Entering directory '/usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic'
warning: the compiler differs from the one used to build the kernel
The kernel was built by: x86_64-linux-gnu-gcc-13 (Ubuntu 13.2.0-23ubuntu4) 13.2.0
You are using: gcc (Ubuntu 13.2.0-23ubuntu4) 13.2.0
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/driver.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/hub.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/userif.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/netif.o
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/userif.c:1091:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018VNetUserIf_Create\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
1091 | VNetUserIf_Create(VNetPort **ret) // OUT
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/netif.c:173:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018VNetNetIf_Create\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
173 | VNetNetIf_Create(char *devName, // IN:
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/bridge.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/procfs.o
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/userif.o: warning: objtool: VNetCsumAndCopyToUser+0x2d: call to csum_partial_copy_nocheck() with UACCESS enabled
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/smac_compat.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/smac.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vnetEvent.o
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vnetUserListener.o
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/bridge.c:258:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018VNetBridge_Create\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
258 | VNetBridge_Create(const char *devName, // IN: name of device (e.g., "eth0")
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/bridge.c:1411:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018VNetBridgeSendLargePacket\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
1411 | VNetBridgeSendLargePacket(struct sk_buff *skb, // IN: packet to split
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vnetUserListener.c:87:1: warning: no previous prototype for \u2018VNetUserListener_Create\u2019 [-Wmissing-prototypes]
87 | VNetUserListener_Create(uint32 classMask, // IN: the listener's class mask
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
LD [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vmnet.o
MODPOST /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/Module.symvers
CC [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vmnet.mod.o
LD [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vmnet.ko
BTF [M] /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vmnet.ko
Skipping BTF generation for /tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only/vmnet.ko due to unavailability of vmlinux
make[1]: Leaving directory '/usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic'
/usr/bin/make -C $PWD SRCROOT=$PWD/. \
MODULEBUILDDIR= postbuild
make[1]: Entering directory '/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only'
make[1]: 'postbuild' is up to date.
make[1]: Leaving directory '/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only'
cp -f vmnet.ko ./../vmnet.o
make: Leaving directory '/tmp/modconfig-14X4lZ/vmnet-only'
Unable to install all modules. See log for details.
Method 2: Downloading and Compiling Patched VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules on Ubuntu/Debian
The GitHub repository mkubecek/vmware-host-modules releases patched versions of the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules regularly so that the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules can be compiled for the latest Linux kernels.
If the official VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules fail to compile on your Ubuntu/Debian system, your only option is to compile and use the patched VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules.
In this section, I will show you how to download patched VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules for the installed VMware Workstation Pro version and compile it on your Ubuntu/Debian system. For demonstration, I am using VMware Workstation Pro v17.5.2 on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Linux kernel version 6.8.0).
First, navigate to the /tmp directory as follows:
$ cd /tmp

Clone the GitHub repository mkubecek/vmware-host-modules with the following command:
$ git clone https://github.com/mkubecek/vmware-host-modules.git
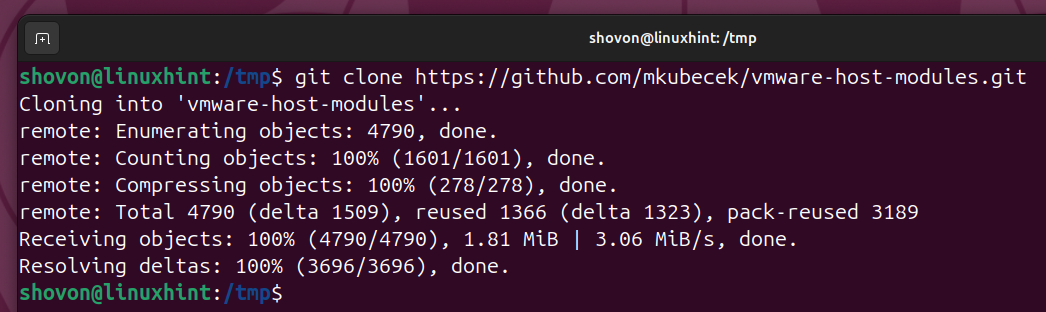
A new directory vmware-host-modules/ should be created. Navigate to the vmware-host-modules/ directory as follows:
$ cd vmware-host-modules/

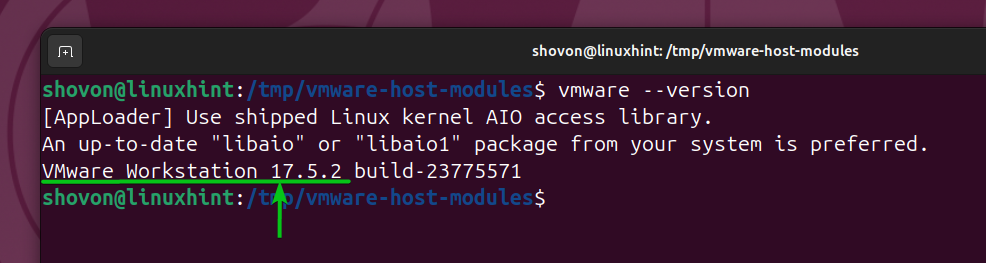
To check the VMware Workstation Pro version you have installed, run the following command:
$ vmware --version
As you can see, I have VMware Workstation Pro v17.5.2 installed on my Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system.
To check the available patched VMware Workstation Pro 17 kernel modules on the clonned GitHub repository, run the following command:
$ git branch --remotes | grep workstation-17
As you can see, VMware Workstation Pro v17.5.2 is not available yet, but v17.5.1 is available. VMware Workstation Pro v17.5.1 kernel modules should work just fine on VMware Workstation Pro v17.5.2.
NOTE: By the time you read this article, patched kernel module should be available for your VMware Workstation Pro version. Or, VMware may fix problems with their official kernel modules and you may no longer need patched VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules.

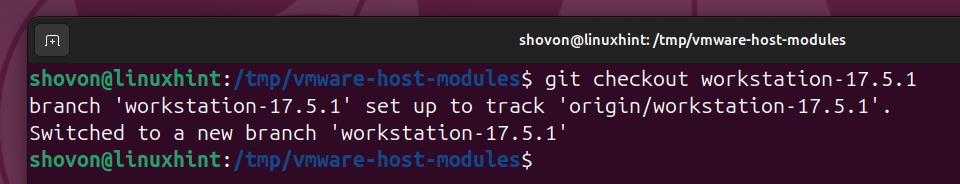
Checkout the workstation-17.5.1 branch as follows:
$ git checkout workstation-17.5.1
You will find two folders vmmon-only/ and vmnet-only/ in the /tmp/vmware-host-modules directory.
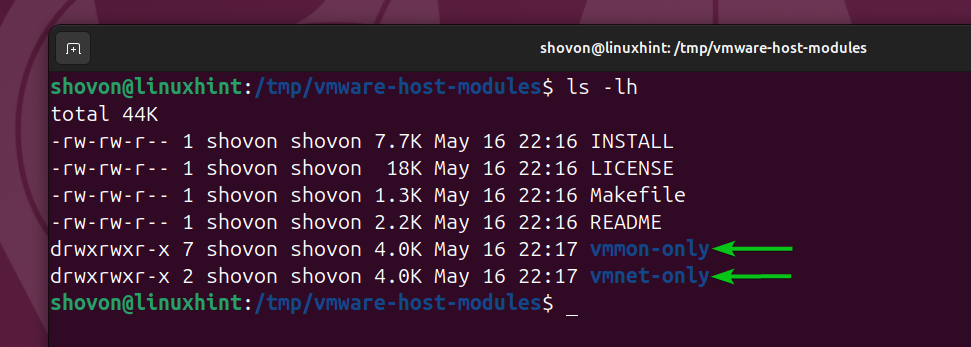
Compress the vmmon-only/ directory to vmmon.tar and vmnet-only/ directory to vmnet.tar as follows:
$ tar -cf vmmon.tar vmmon-only/
$ tar -cf vmnet.tar vmnet-only/
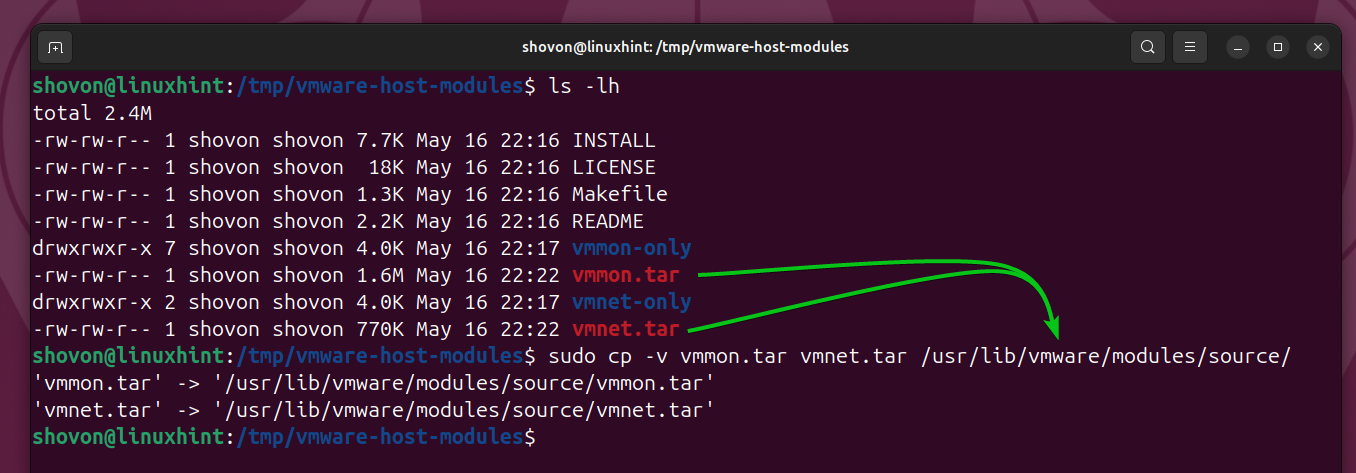
Copy the compressed vmmon.tar and vmnet.tar file from the /tmp/vmware-host-module directory to /usr/lib/vmware/modules/source directory to replace the official VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules with the patched kernel modules.
$ sudo cp -v vmmon.tar vmnet.tar /usr/lib/vmware/modules/source/
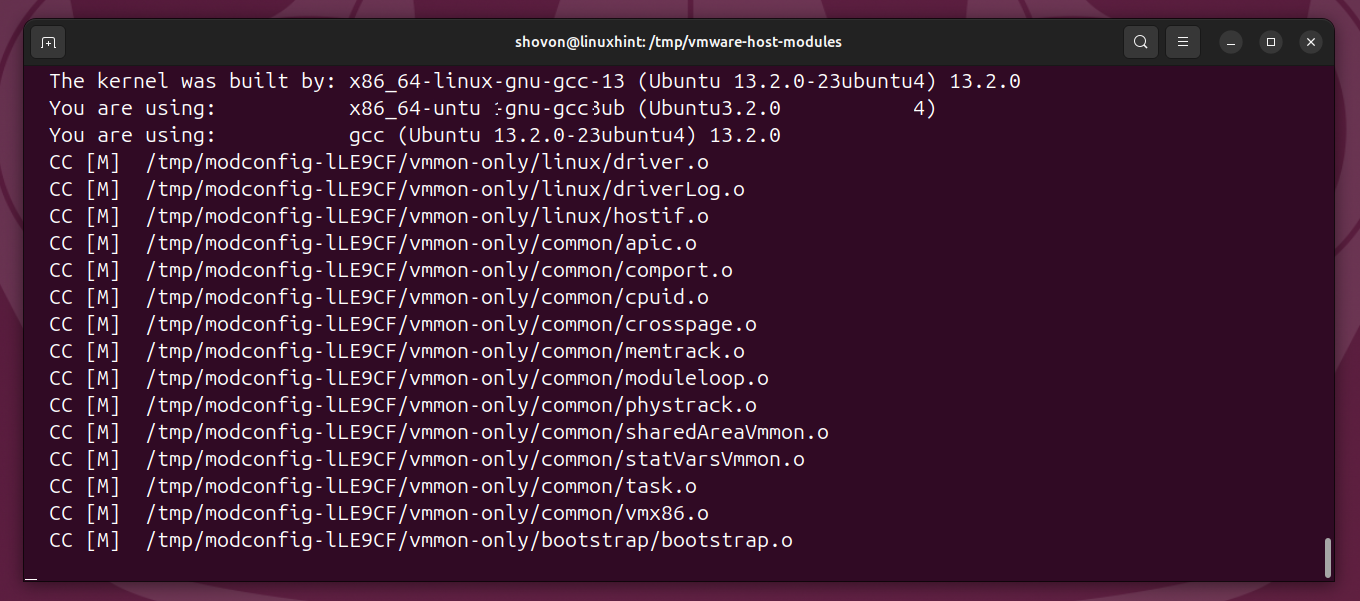
To compile the patched VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules, run the following command:
$ sudo vmware-modconfig --console --install-all
The VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules are being compiled. It will take a few seconds to complete.
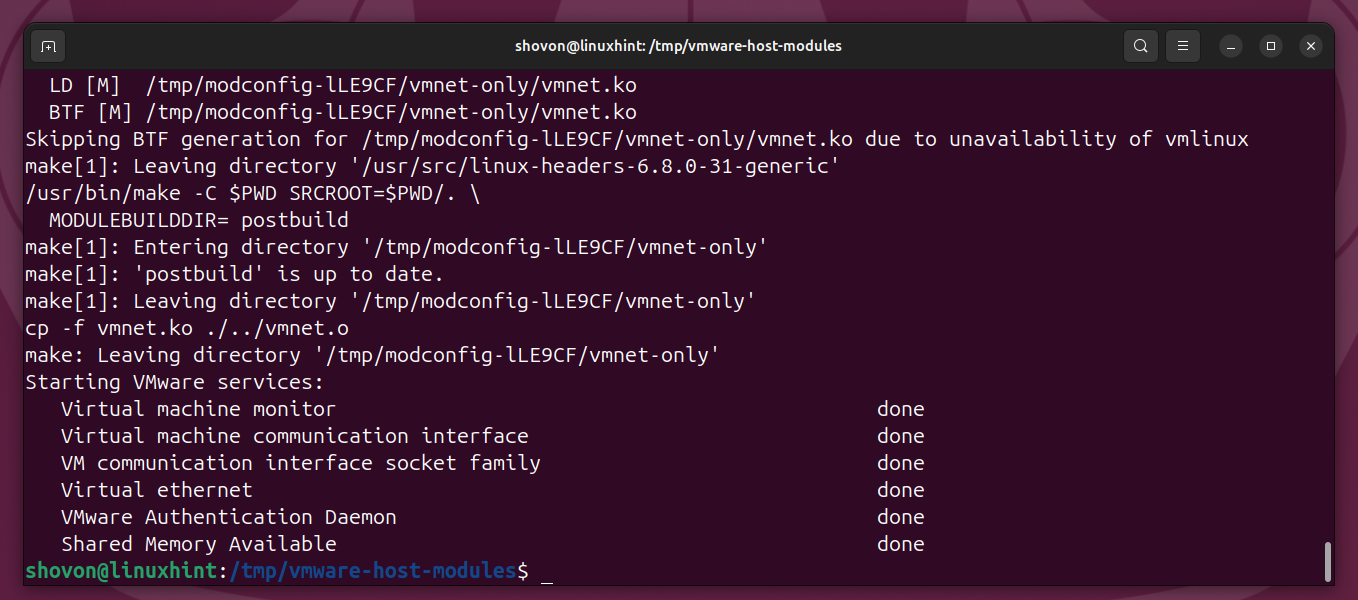
At this point, the patched VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules should be compiled and installed.
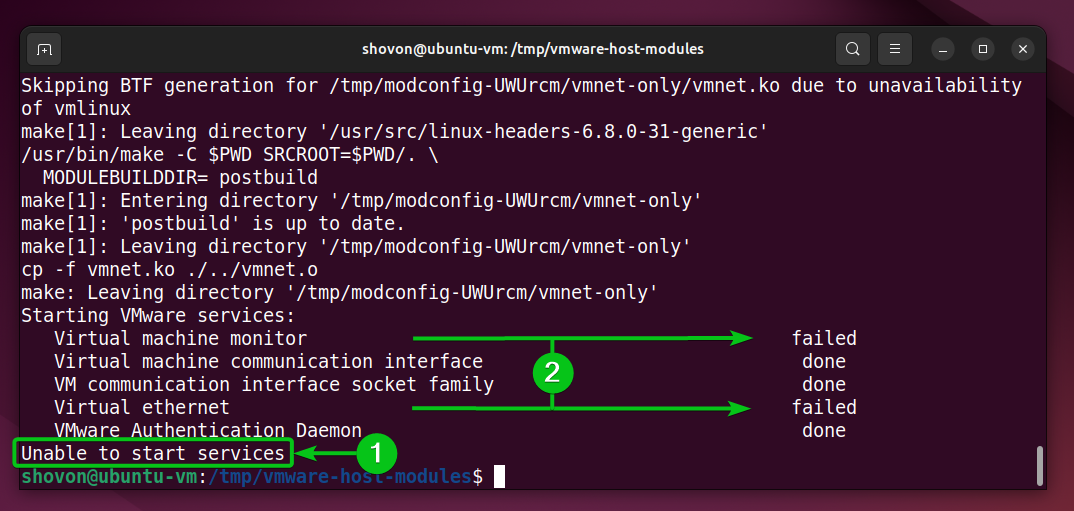
Fixing VMware Workstation Pro Services Fail to Start on Ubuntu/Debian
VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules won’t load on UEFI Secure Boot enabled Ubuntu/Debian systems, resulting in VMware Workstation Pro services failing to start. Because of that, you will see the marked errors just after compiling the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules.
To solve this problem, disable UEFI Secure Boot from the BIOS/UEFI Firmware of your motherboard. Or, sign the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules for your UEFI secure boot enabled Ubuntu/Debian system.
Conclusion
In this article, I have shown you how to compile the official VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules on Ubuntu/Debian. I have also shown you how to downlaod and compile patched VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules on Ubuntu/Debian in case the official VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules fail to compile. Finally, I have discussed the problems you may face with loading the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules and starting the VMware Workstation Pro systemd services on UEFI Secure Boot enabled Ubuntu/Debian systems and linked to additional articles demonstrating the process of solving the problems.
References
More...