For VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules to load on UEFI Secure Boot enabled Linux systems, you must sign them manually. Unsigned VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules won’t load, resulting in VMware Workstation Pro services failing to start.
As you can see, VMware Workstation Pro services failed to start after the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules were compiled successfully.
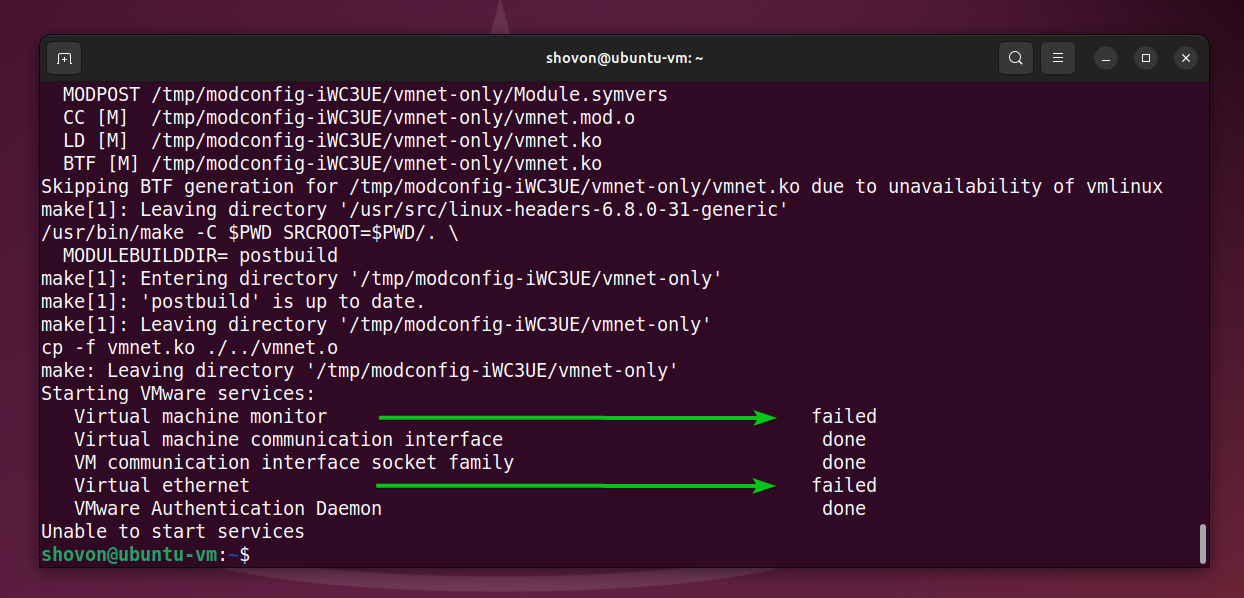
The vmware systemd service also failed to start.
$ sudo systemctl status vmware
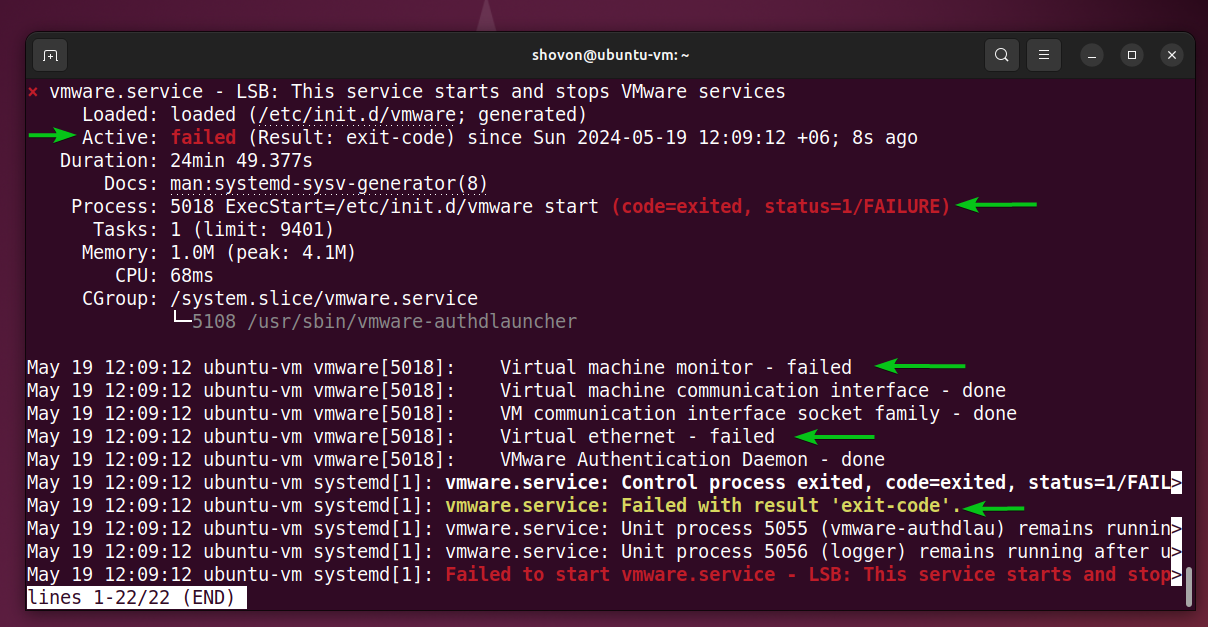
One solution to this problem is to disable UEFI secure boot from the BIOS/UEFI firmware of your motherboard. But if you don’t want to disable UEFI secure boot on your computer, then you must generate a kernel module signing key and sign the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules using the generated key.
In this article, I will show you how to generate a kernel module signing key and sign the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules with it so that the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules load correctly on UEFI secure boot enabled Linux systems.
Table of Contents
- Generating a UEFI Kernel Module Signing Key
- Finding the Full Path of the sign-file Kernel Script
- Signing the VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules for UEFI Secure Boot
- Adding the UEFI Kernel Signing Keys to the shim
- Enrolling the UEFI Kernel Signing Keys
- Checking if VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules are Signed for UEFI Secure Boot
- Conclusion
- References
Generating a UEFI Kernel Module Signing Key
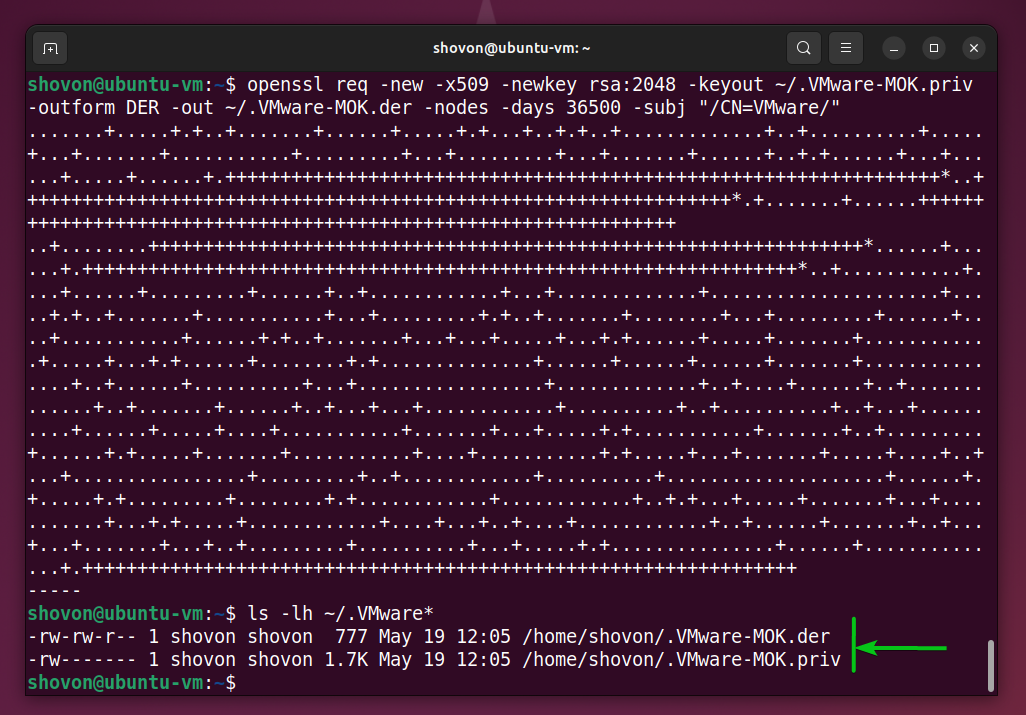
To generate a new UEFI kernel module signing key pair and save them in the ~/.VMware-MOK.priv and ~/.VMware-MOK.der file, run the following command:
$ openssl req -new -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout ~/.VMware-MOK.priv -outform DER -out ~/.VMware-MOK.der -nodes -days 36500 -subj "/CN=VMware/"
As you can see a new UEFI kernel module signing key pair .VMware-MOK.priv and .VMware-MOK.der is created in my login user’s home directory.
$ ls -lh ~/.VMware*
Finding the Full Path of the sign-file Kernel Script
To sign the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules using the generated key pair, you need the sign-file kernel script. The sign-file kernel script is available in different path in different Linux distributions.
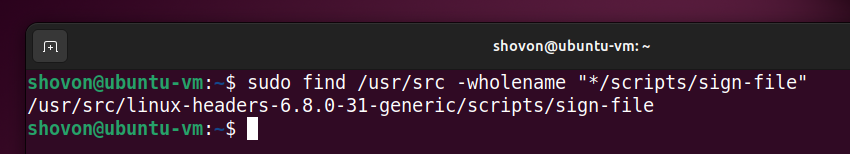
To find the full path of the sign-file kernel script on your Linux distribution, run the following command:
$ sudo find /usr/src -wholename "*/scripts/sign-file"
On my Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system, the sign-file kernel script is in path /usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic/scripts/sign-file.
Signing the VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules for UEFI Secure Boot
To sign the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules vmmon and vmnet using the key pairs ~/.VMware-MOK.priv and ~/.VMware-MOK.der with the sign-file kernel script, run the following commands:
$ sudo /usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic/scripts/sign-file sha256 ~/.VMware-MOK.priv ~/.VMware-MOK.der $(modinfo -n vmmon)
$ sudo /usr/src/linux-headers-6.8.0-31-generic/scripts/sign-file sha256 ~/.VMware-MOK.priv ~/.VMware-MOK.der $(modinfo -n vmnet)
Adding the UEFI Kernel Signing Keys to the shim
Once the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules are signed with the generated key pairs ~/.VMware-MOK.priv and ~/.VMware-MOK.der, you must add/import the ~/.VMware-MOK.der file to the UEFI shim and enroll it from the UEFI firmware of your computer.
To add/import the ~/.VMware-MOK.der file to the UEFI shim, run the following command:
$ sudo mokutil --import ~/.VMware-MOK.der
Type in a password of your choice and press .
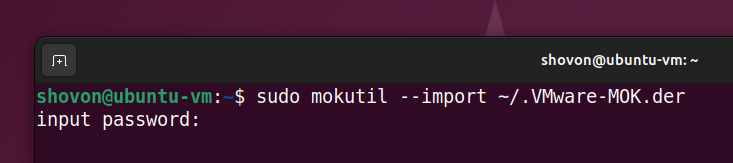
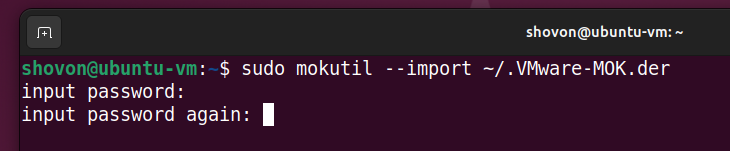
Retype the password and press . The ~/.VMware-MOK.der file should be added/imported to the UEFI shim.
Enrolling the UEFI Kernel Signing Keys
To enroll the key (~/.VMware-MOK.der) imported to the UEFI shim, reboot your Linux system as follows:
$ sudo reboot
You will see a similar shim UEFI key management window.
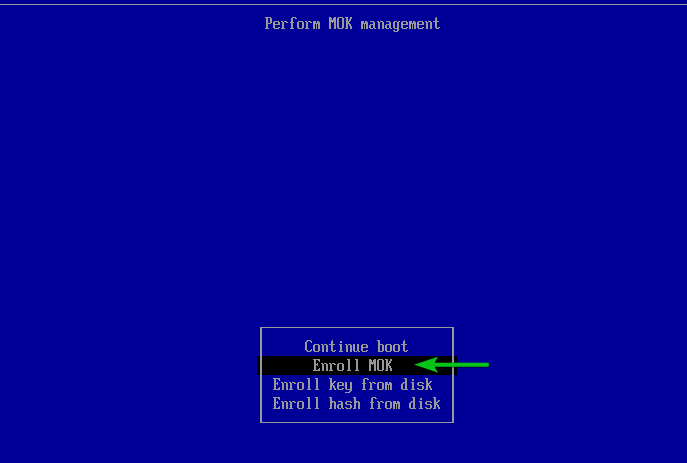
Press any key to perform MOK management.

Select Enroll MOK and press .
To view the key being enrolled, select View key and press .

The key that you are about to enroll should be displayed.
To go back, press .
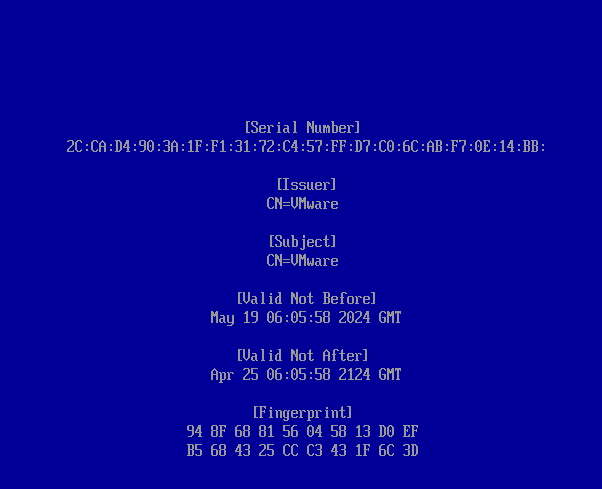
To enroll the key, select Continue and press .

Select Yes and press .

Type in the password that you’ve set while adding the generated key to the UEFI shim and press .

Select Reboot and press .

Checking if VMware Workstation Pro Kernel Modules are Signed for UEFI Secure Boot
Once your Linux system boots, you can verify if the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules are signed just by checking if they are loaded at boot time with the command below:
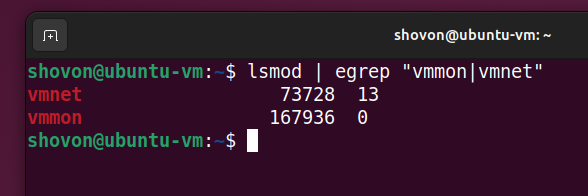
$ lsmod | egrep "vmmon|vmnet"
If the vmmon and vmnet kernel modules are loaded, then the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules are successfully signed for your UEFI secure boot enabled Linux system.
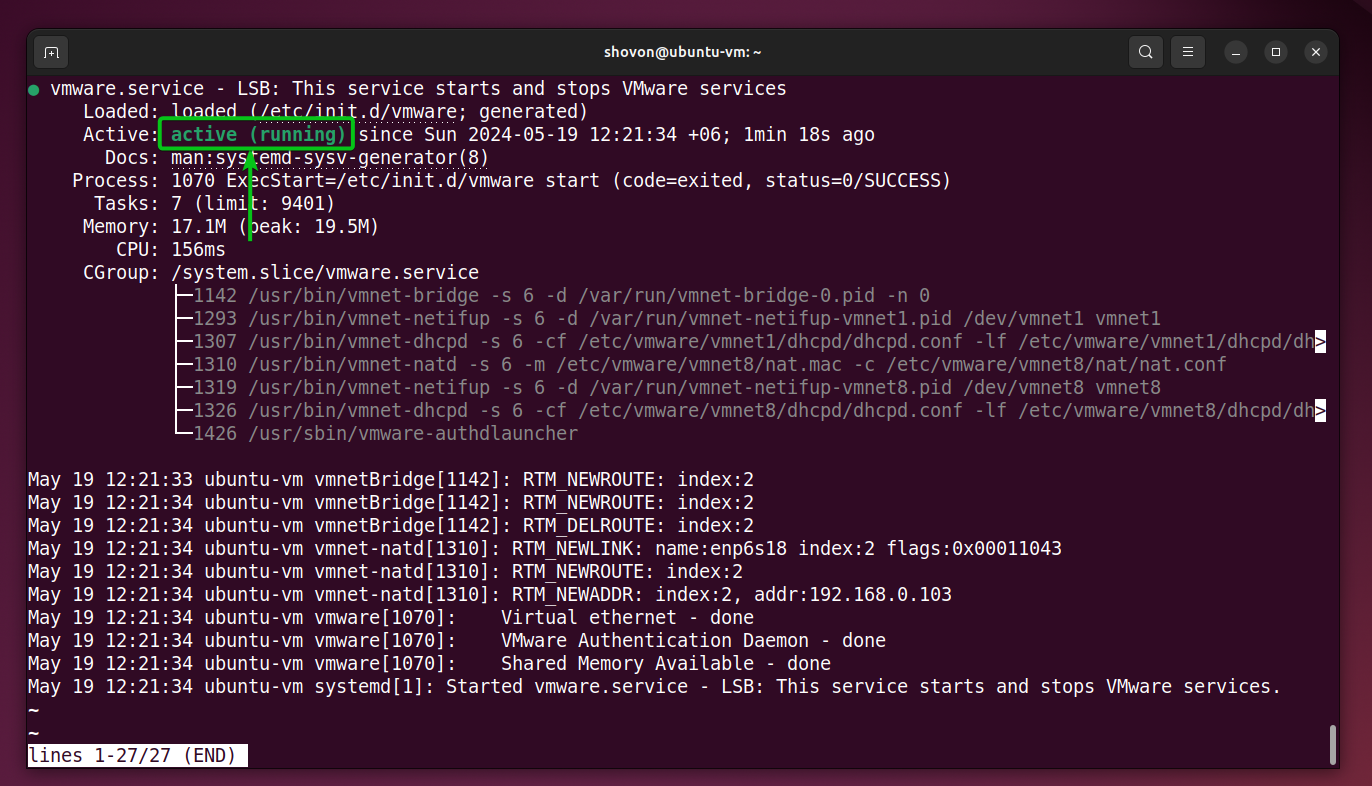
If the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules are signed, the vmware systemd service should be running on your Linux system.
$ sudo systemctl status vmware
Conclusion
In this article, I have shown you how to sign the VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules so that they can be loaded on UEFI secure boot enabled Linux systems. Without signed VMware Workstation Pro kernel modules, VMware Workstation Pro won’t work on UEFI secure boot enabled systems.
References
- Instructions on signing VirtualBox and VMware modules for Secure Boot
- Re-signing kernel modules after update – VMMON – Ask Ubuntu
More...