WOL – Wake-on-LAN is a feature of the Synology NAS that allows you to turn on your Synology NAS from any computer on the same network as your Synology NAS without needing to press the power button of your Synology NAS.
If you want to keep your Synology NAS locked in a cabinet, or on top of a shelf that is very hard to reach (due to height), you may not have easy access to the power button of your Synology NAS. In that case, you will be able to use WOL (Wake-On-LAN) to turn on your Synology NAS remotely from other devices.
You can use the Synology Assistant app to send WOL signal to your Synology NAS to turn it on. You can also use a WOL Client on your computer to send a WOL signal to your Synology NAS to turn it on.
In this article, I will show you how to send a WOL (Wake-On-LAN) signal to your Synology NAS from the Command-Line of popular Linux distributions (using a Linux WOL client) to power on your Synology NAS remotely.
Table of Contents
- Enabling Wake-On-LAN (WOL) on a Synology NAS
- Finding MAC Address of Network Interface of Synology NAS with WOL Enabled
- Installing WOL Client on Ubuntu/Debian
- Installing WOL Client on Fedora
- Installing WOL Client on openSUSE
- Installing WOL Client on Arch Linux/Manjaro
- Powering On Synology NAS Remotely from the Ubuntu/Debian Command-Line using wakeonlan
- Powering On Synology NAS Remotely from Linux Command-Line using wol
- Conclusion
Enabling Wake-On-LAN (WOL) on a Synology NAS
To enable the Wake-on-LAN (WOL) feature on your Synology NAS, visit the DSM web interface of your Synology NAS from your favorite web browser.
From the DSM web interface, open the Control Panel app and click on Hardware & Power.
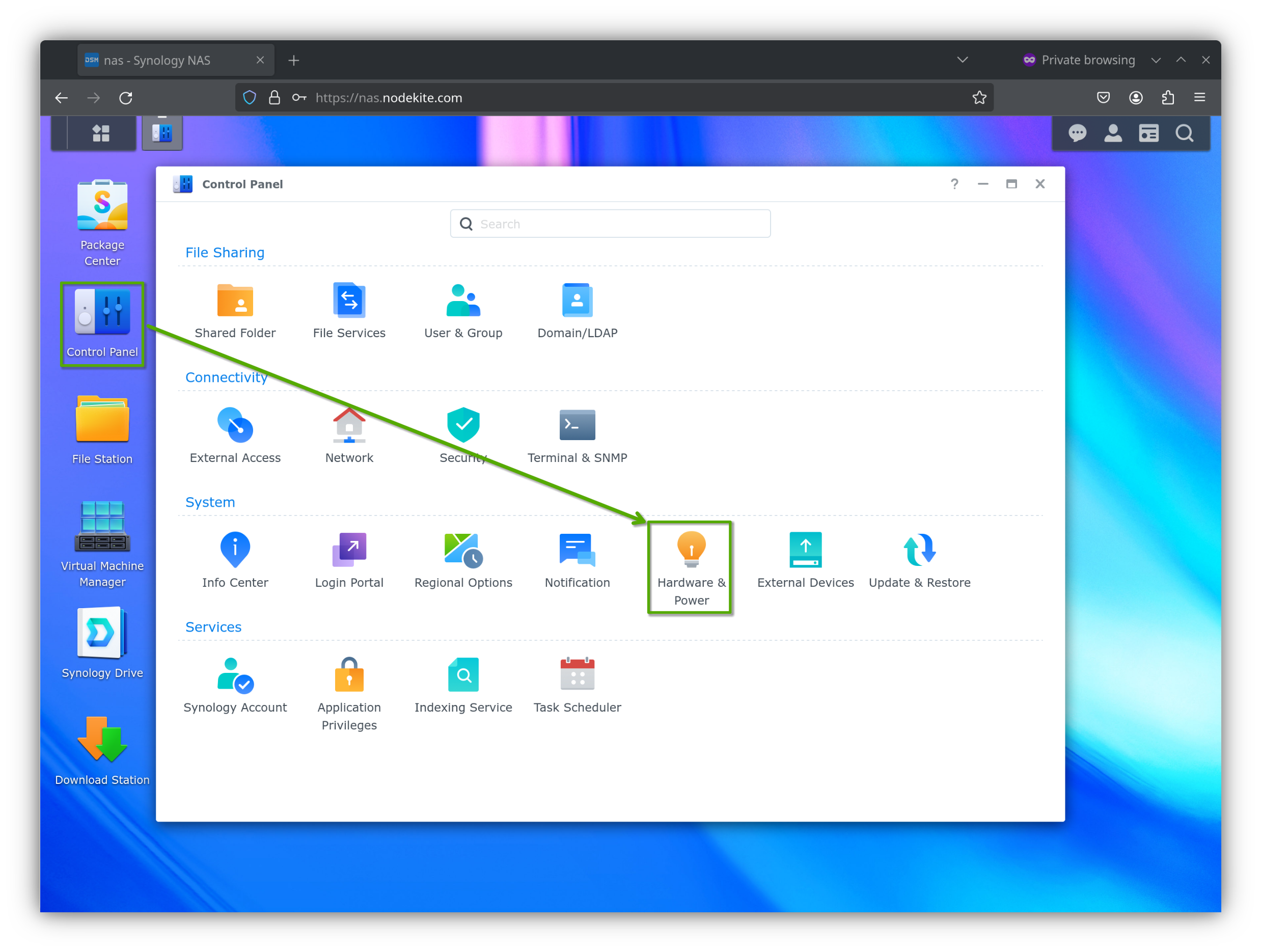
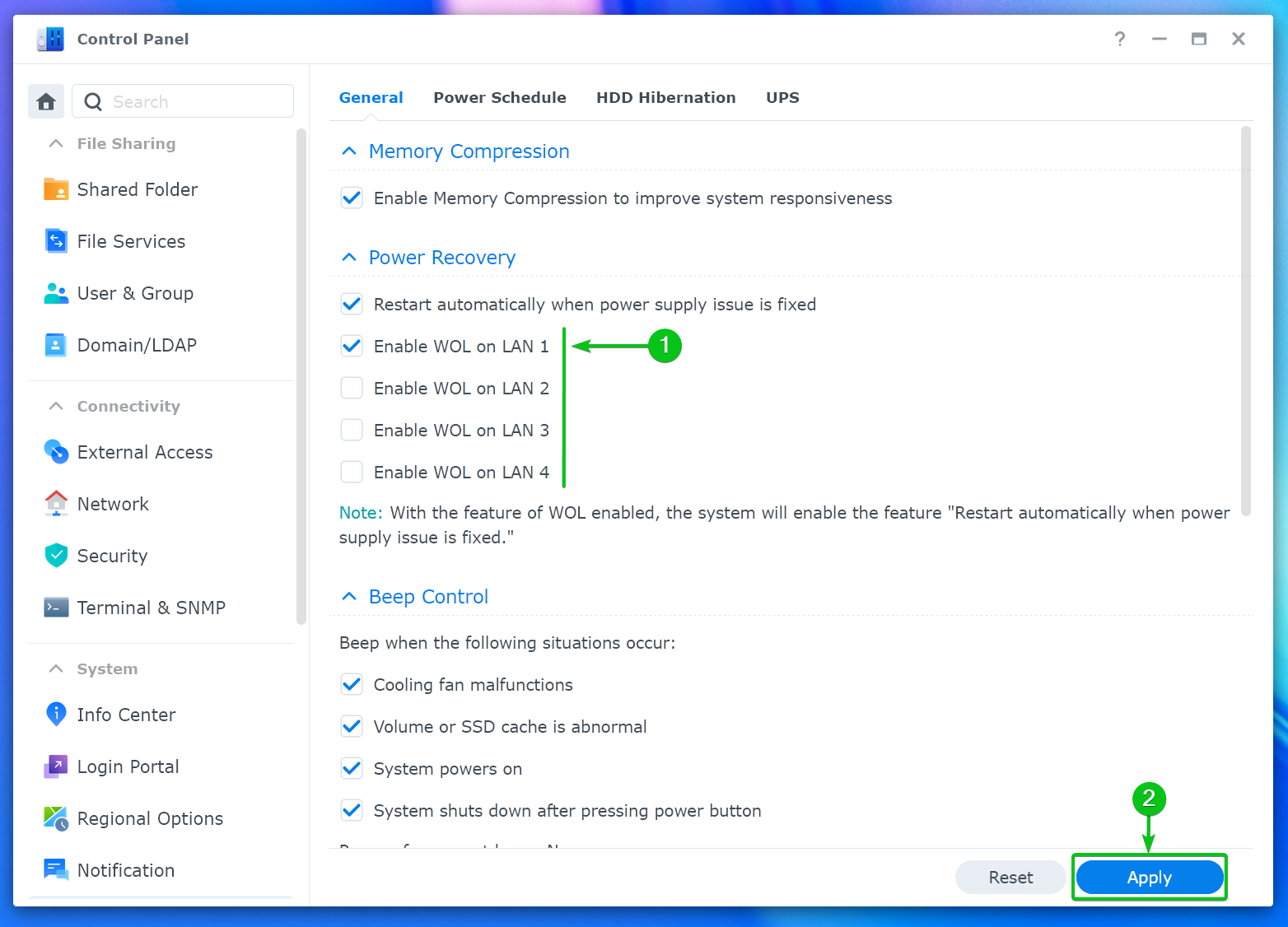
From the Power Recovery section of the General tab, you can enable Wake-on-LAN (WOL) for one or more network interfaces of your Synology NAS[1].
I am using only the first network interface (LAN 1) of my Synology NAS. So, I have ticked Enable WOL on LAN 1 to enable Wake-on-LAN for only the first network interface (LAN 1) of my Synology NAS.
Once you’re done, click on Apply to save the changes[2].
Finding MAC Address of Network Interface of Synology NAS with WOL Enabled
To send a Wake-on-LAN (WOL) signal to your Synology NAS remotely, you need to know the MAC address of a WOL enabled network interface of your Synology NAS.
Read this article if you need any assistance in finding the MAC address of the network interfaces of your Synology NAS.
Installing WOL Client on Ubuntu/Debian
On Ubuntu/Debian, you will find the wakeonlan WOL client in the official package repository. So, it’s easy to install.
First, update the APT package database cache with the following command:
$ sudo apt update
To install the wakeonlan WOL client on Ubuntu/Debian, run the following command:
$ sudo apt install wakeonlan -y
wakeonlan WOL client should be installed on your Ubuntu/Debian system.

Read this section for instructions on powering on your Synology NAS remotely from the command line using the wakeonlan WOL client.
Installing WOL Client on Fedora
On Fedora Linux, you will find the wol WOL client in the official package repository. So, it’s easy to install.
First, update the DNF package database cache with the following command:
$ sudo dnf makecache

To install the wol WOL client on Fedora Linux, run the following command:
$ sudo dnf install wol -y
The wol WOL client should be installed.

Read this section for instructions on powering on your Synology NAS remotely from the command line using the wol WOL client.
Installing WOL Client on openSUSE
On OpenSUSE Linux, you will find the wol WOL client in the official package repository. So, it’s easy to install.
First, update the Zypper package database cache with the following command:
$ sudo zypper refresh
To install the wol WOL client on openSUSE Linux, run the following command:
$ sudo zypper install wol
In this case, the wol client tool is installed by default on my openSUSE Leap 15.5 system. If it’s not installed in your case, the zypper package manager will install it for you.

Read this section for instructions on powering on your Synology NAS remotely from the command line using the wol WOL client.
Installing WOL Client on Arch Linux/Manjaro
On Arch Linux, Manjaro, and other Arch-Linux based Linux distributions, you will find the wol WOL client in the official package repository. So, it’s easy to install.
To install the wol WOL client tool on Arch Linux/Manjaro, run the following command:
$ sudo pacman -Sy wol
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press .
The wol WOL client should be installed.
Read this section for instructions on powering on your Synology NAS remotely from the command line using the wol WOL client.
Powering On Synology NAS Remotely from the Ubuntu/Debian Command-Line using wakeonlan
If you’re using one of the Linux distributions listed below, then you will be using the wakeonlan WOL client to power on your Synology NAS remote.
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Linux Mint
- Elementary OS
- Deepin Linux
- Other Ubuntu/Debian-based Linux distributions
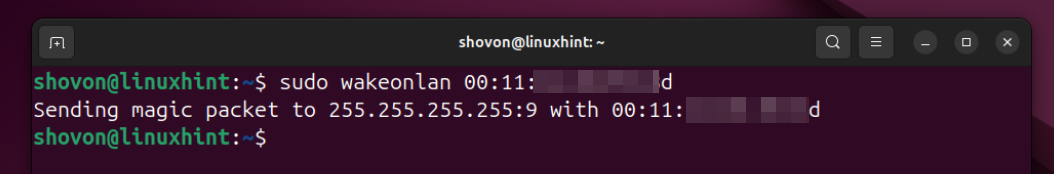
If the MAC address of the WOL enabled network interface of your Synology NAS is 00:11:aa:bb:cc:dd, then you can remotely power on your Synology NAS from Ubuntu/Debian using the wakeonlan WOL client as follows:
$ sudo wakeonlan 00:11:aa:bb:cc:dd
For more information on the wakeonlan WOL client, read the wakeonlan help page.
$ wakeonlan --help
Powering On Synology NAS Remotely from Linux Command-Line using wol
If you’re using one of the Linux distributions listed below, then you will be using the wakeonlan WOL client to power on your Synology NAS remote.
- Fedora Linux
- Arch Linux
- Manjaro
- openSUSE
- Other Linux distributions based on Fedora and Arch Linux.
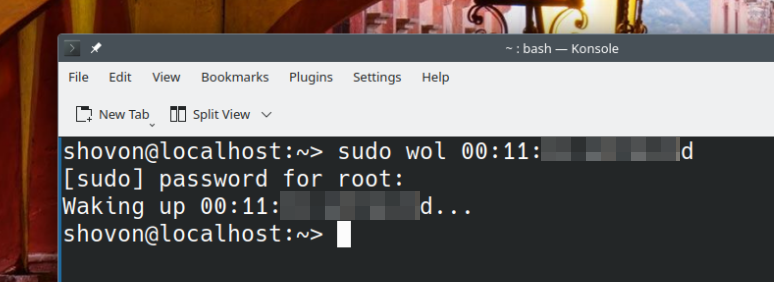
If the MAC address of the WOL enabled network interface of your Synology NAS is 00:11:aa:bb:cc:dd, then you can remotely power on your Synology NAS from Ubuntu/Debian using the wol WOL client as follows:
$ sudo wol 00:11:aa:bb:cc:dd
For more information on the wol WOL client, read the wol help page.
$ wol --help

Conclusion
In this article, I have shown you how to enable Wake-on-LAN (WOL) for a network interface of your Synology NAS. I have also shown you how to install a WOL client on popular Linux distributions such as Ubuntu/Debian (and Ubuntu/Debian-based Linux distributions like Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Deepin Linux), Fedora Linux, openSUSE, and Arch Linux (and Arch-based Linux distributions like Manjaro Linux). Finally, I have shown you how to send a Wake-on-LAN (WOL) signal to your Synology NAS using the wakeonlan/wol command-line tool from Linux to power on your Synology NAS remotely.
More...