In bash scripting, environment variables are used to save and manage the data to modify the processes in the system. Using the bash scripts, you can use the environment variables to configure the system process. Environment variables also offer security and transmit the information from one script to another.
Hence, there are multiple uses of environment variables that you can use to enhance the automation in the Linux system. So, if you want to learn the simple ways to set and use environment variables in a bash script, this tutorial is for you. Here, we have included various examples and use cases of environment variables in bash.
Basics of Setting Up Environment Variable
You directly set the environment variable from the terminal through the export command. For example, let’s create an environment variable “NOTE” having a special text “Welcome to Ubuntu Machine”:
export NOTE="Welcome to Ubuntu Machine"

Once you are done, it is time to use the “NOTE” variable in the script:
#!/bin/bash
echo $NOTE
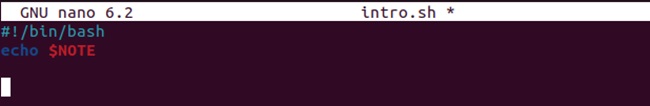
Now, let’s execute the script and print the result:
./intro.sh

In case you want to create an environment variable in the script, and here is an example to do it:
#!/bin/bash
export UPDATE="sudo apt update"
echo $NOTE
$UPDATE
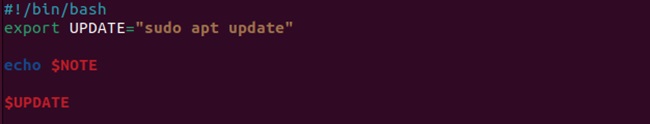
Now, you can run the above script to get the desired results:
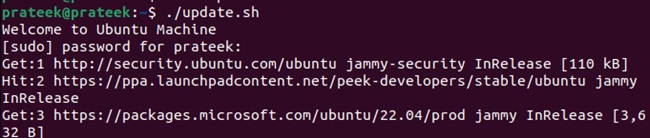
Similarly, you can create a temporary variable that will only work with the single script execution. For example, let’s create two environment variables: WELCOME and UPGRADE:
Now, you can declare the variable while executing the script:
#!/bin/bash
echo $WELCOME
Let's upgrade your system
$UPGRADE

Now, you can declare the variable while executing the script:
WELCOME="Welcome $USER" UPGRADE="sudo apt update && apt upgrade ./script.sh
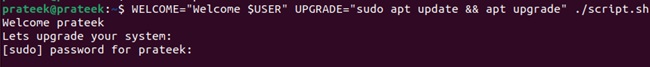
You can access the environment variables directly from the terminal using the following command:
echo $<environment_variable>

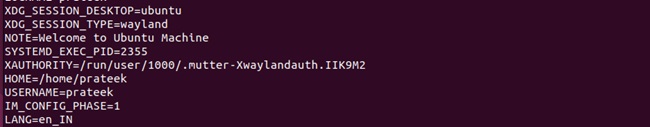
Moreover, you can check all the environment variables available in your system:
printenv
Advanced Approaches to Set Environment
If you want to create an environment variable that should be available after the script execution or the terminal session, then please use the below command:
echo 'export VAR="information"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
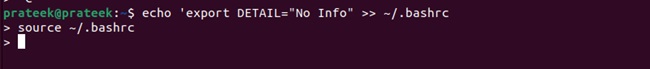
The above command will add the export to the .bashrc file.
Wrapping Up
So, this was all about the ways to set and use the environment variables in the bash script. We have included various types of methods to set up the environment variables and also use them after the specific terminal session.
Moreover, we recommend you explore your skills and create unique environment variables to automate the tasks using the bash scripting. If you encounter some issues while using the environment variable, then you can check out our guide to resolve the problems with the environment variable.
More...