The dd command, or data duplicator, is a robust and versatile utility famous for its disk manipulation features. While its primary purpose is to create disk images, it also lets you clone data, convert file formats, take backups, and more.
Whether you’re a Linux beginner or an experienced user, understanding the various applications of the dd command can be beneficial. In this short tutorial, we’ll explore multiple examples of the dd command in Linux you can learn with no hassles.
Create an Image of a Hard Disk Using dd Command
Creating an image of a hard disk using the dd command is the foremost example. This image acts as a backup of a storage device, and you can create one by executing the below command:
dd if=/path/to/source/partition of=~/drive.img bs=8M
Let’s break the above command:
- if (Input File): Specifies the source file or the drive from where you want it to read the data.
- of (Output File): Specifies the target file or the drive where you want to write the data.
- bs (Block Size): Specifies the size(in MBs) of blocks to use for the I/O operations.
- count: Sets the number of blocks to copy.
- Seek: Seek the input value of N and skip the N number of blocks before writing any data.
- skip: Skips N number of blocks before reading any data.
In case you don’t know how to find the path of the hard disk, you can run the df command to list all the disks and their current storage space:
df
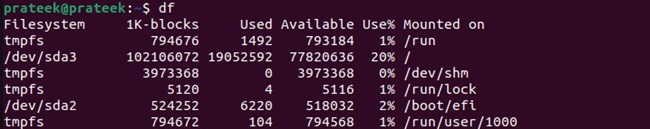
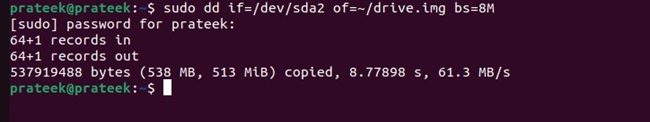
Now, let’s take an example to create image of a /dev/sda2 using the following command:
sudo dd if=/dev/sda2 partition of=~/drive.img bs=8M
If you want to restore the disk image, please run the below dd command:
dd if=~/drive.img of=/path/to/target/partition

You can also use the dd command to create a bootable USB drive from an ISO image, like:
dd if=~/drive.iso of=/path/of/USB_drive bs=4M status=progress && sync

Here, we use the “status=progress” option to display the progress of the data transfer, the amount of data copied, and its transfer speed. The “sync” option reduces the risk of data loss or corruption and ensures the data gets completely written to the target drive.
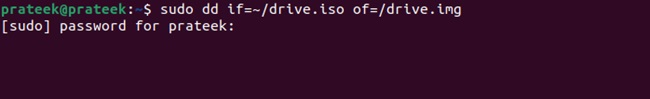
If you instead want to convert an ISO image file to a raw disk image file, use:
dd if=~/drive.iso of=~/drive.img
For the sake of data backup or any other similar purpose, you can use the below dd command to clone a disk:
dd if=/source/disk of=/target/disk bs=8M
Replace ‘/source/disk’ and ‘/target/disk’ with the actual source and target disks, respectively. This command will generate an exact source copy at the target path.
Furthermore, if you want to convert any disk partition into an ISO image file, run the following:
dd if=/source/disk of=~/iso_image.iso bs=2M
Here, replace ‘iso_image’ with the name of the ISO file you intend to create.
Wrapping Up
The dd command is a powerful utility for creating, modifying, and restoring disk images. You can master it to perform disk cloning and data conversion tasks with ease. Therefore, this tutorial demonstrates multiple examples of the dd command in Linux. You can experiment the above commands to make disk images, restore disk data from images, create bootable drives, clone a disk, and much more.
More...