OpenCL is an open-source library for running compute tasks on GPUs. OpenCL enables 3D hardware acceleration for supported applications (i.e. LibreOffice) using the GPU hardware (i.e. Intel iGPU) you have installed on your computer. So, unless OpenCL is installed, OpenCL-supported applications (i.e. LibreOffice) will not have hardware acceleration enabled and may not perform well (i.e. UI might be laggy) as a result. So, it’s a good idea to install OpenCL on your newly installed Fedora 40 (or later) desktop operating system.
In this article, I am going to show you how to install OpenCL for your Intel iGPU on Fedora 40 (or later).
Table of Contents
- Updating DNF Package Repository Cache on Fedora
- Installing OpenCL for Intel GPU on Fedora
- Checking if OpenCL is Working on Fedora
- Conclusion
- References
Updating DNF Package Repository Cache on Fedora
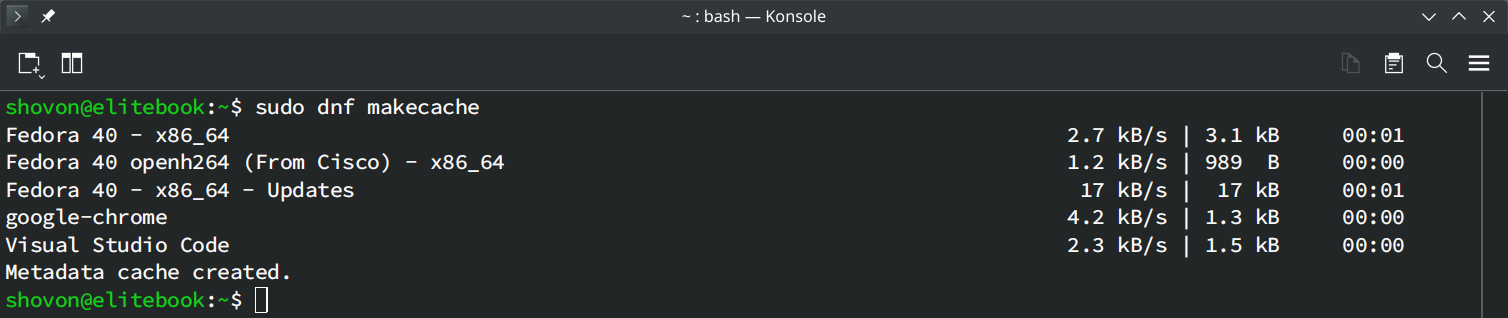
To update the DNF package repository cache on Fedora 40 (and future versions), run the following command:
$ sudo dnf makecache
Installing OpenCL for Intel GPU on Fedora
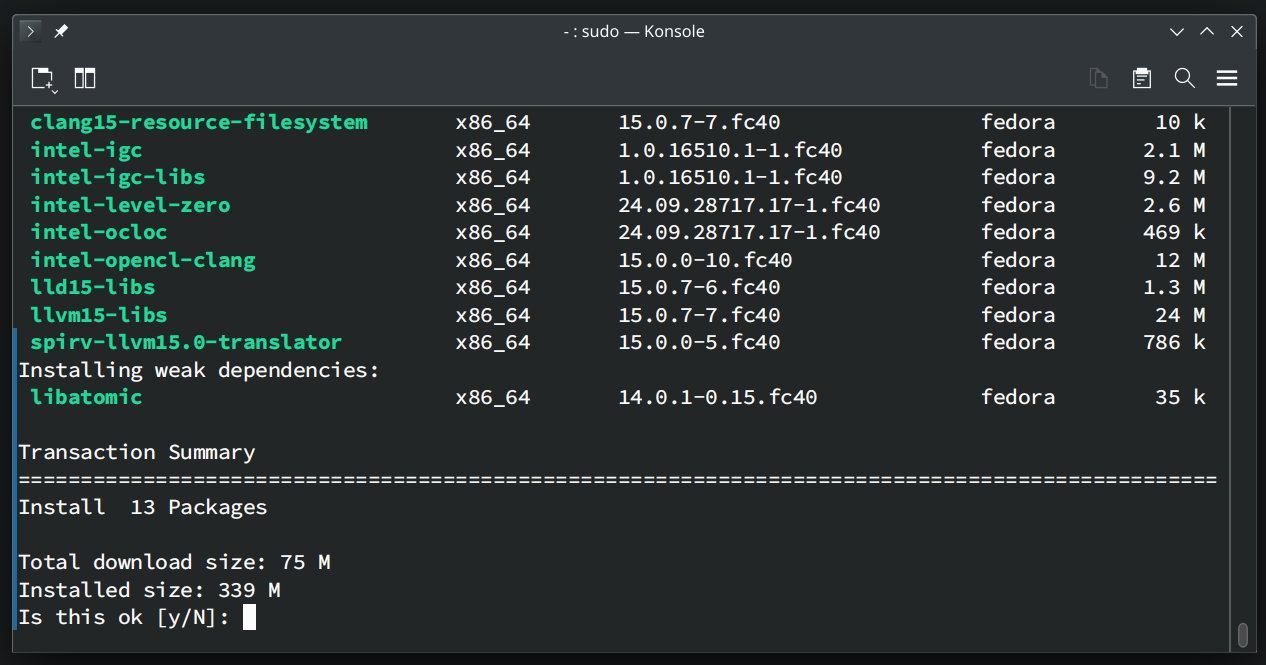
To install OpenCL libraries for Intel GPUs, run the following command:
$ sudo dnf install intel-compute-runtime intel-opencl
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press .
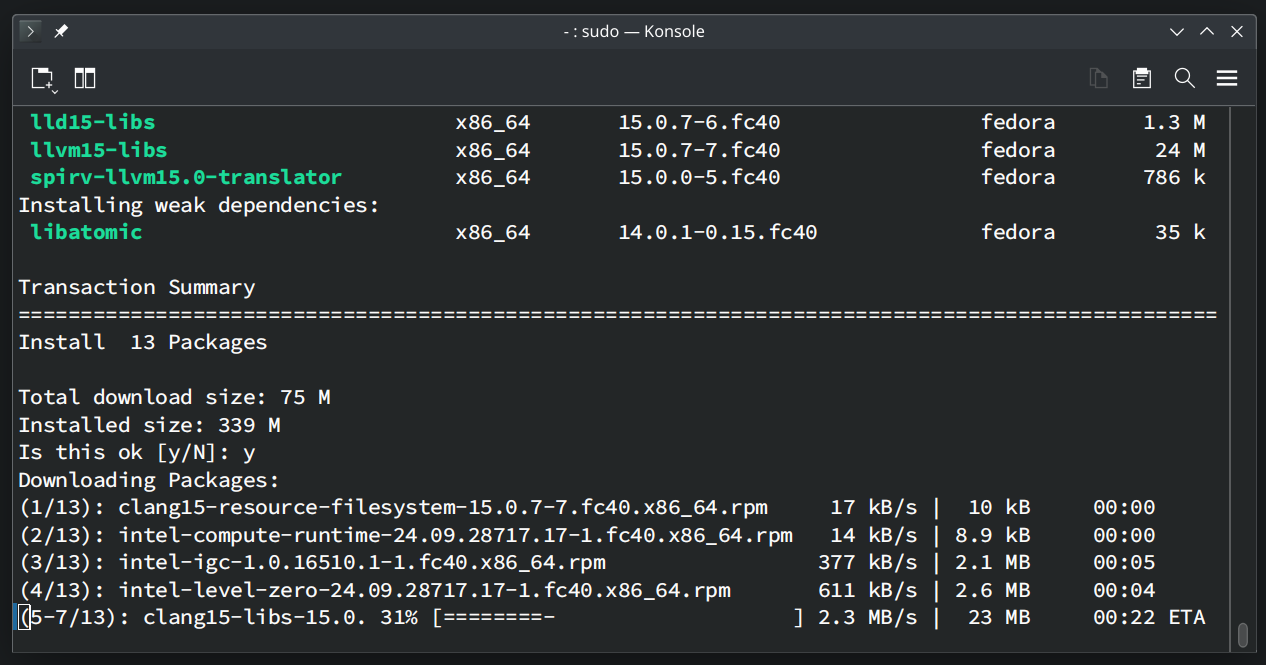
OpenCL for Intel GPU is being installed. It will take a few seconds to complete.
OpenCL libraries for Intel GPU should be installed on your Fedora system.
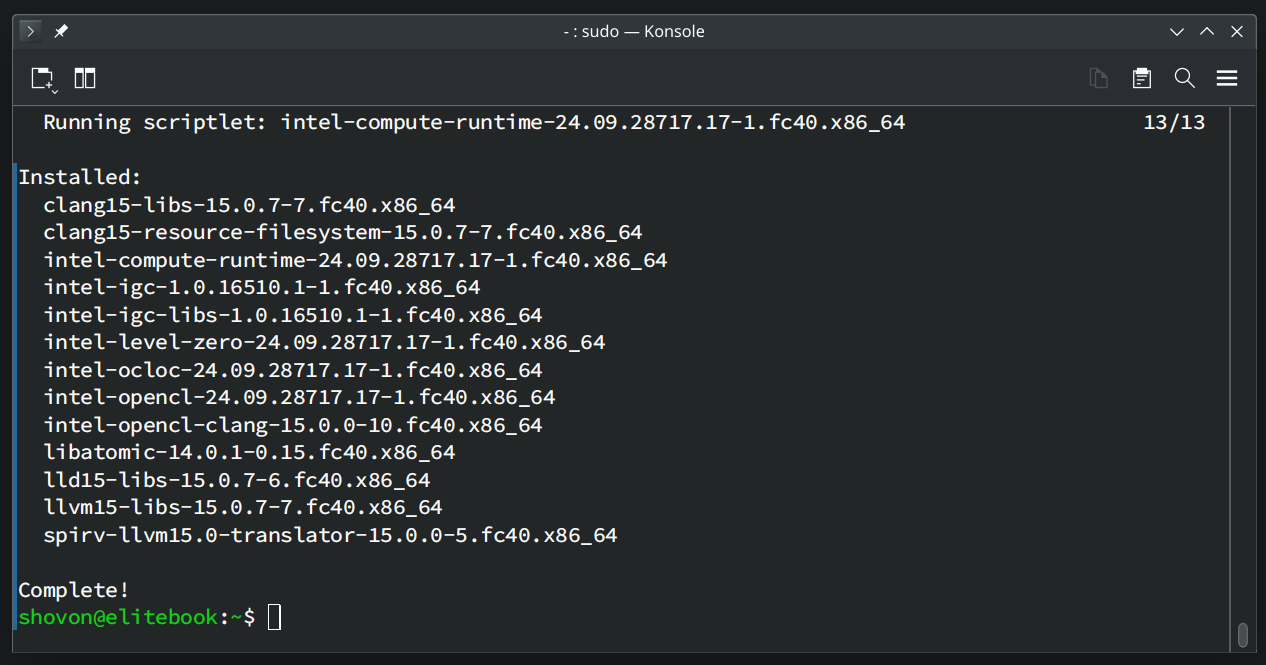
For the changes to take effect, restart your computer with the following command:
$ sudo reboot
Checking if OpenCL is Working on Fedora
To check if OpenCL is working on your Fedora system, run the command below:
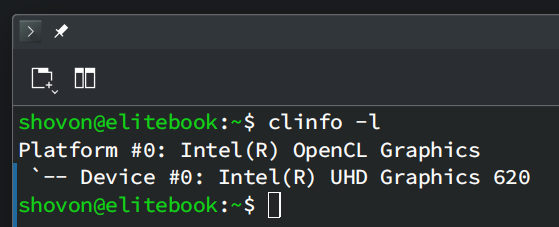
$ clinfo -l
If OpenCL is working, your Intel GPU should be listed as an OpenCL device as shown in the screenshot below.
Conclusion
In this article, I have shown you how to install OpenCL for Intel GPU on your Fedora 40 (or later) operating system so that OpenCL-supported applications can perform better using OpenCL hardware acceleration on Fedora.
References
More...