You can passthrough USB devices from your Proxmox VE host to any of your Proxmox VE virtual machines (VMs) and access the USB devices from the Proxmox VE virtual machines in the same way as you do on any other computers.
In this article, I will show you how to passthrough USB devices to a Proxmox VE virtual machine (VM) and access it from the virtual machine.
Table of Contents
- Enabling USB Hotplug for Proxmox VE Virtual Machines (VMs)
- Proxmox VE USB Passthrough Methods
- Passthrough USB Devices to Proxmox VE Virtual Machines (VMs)
- Accessing the USB Device in the Proxmox VE Virtual Machine (VM)
- Removing the USB Device from the Proxmox VE Virtual Machine (VM)
- Conclusion
- References
Enabling USB Hotplug for Proxmox VE Virtual Machines (VMs)
USB Hotplug is a feature of Proxmox VE that allows you to add/remove USB devices in the virtual machine on the fly (even when the virtual machine is powered on). I highly recommend you to enable USB Hotplug on the Proxmox VE virtual machines where you need access to different USB devices.
To configure Hotplug settings for a Proxmox VE virtual machine, navigate to the Options section of the VM[1], select Hotplug[2] and click on Edit[3].
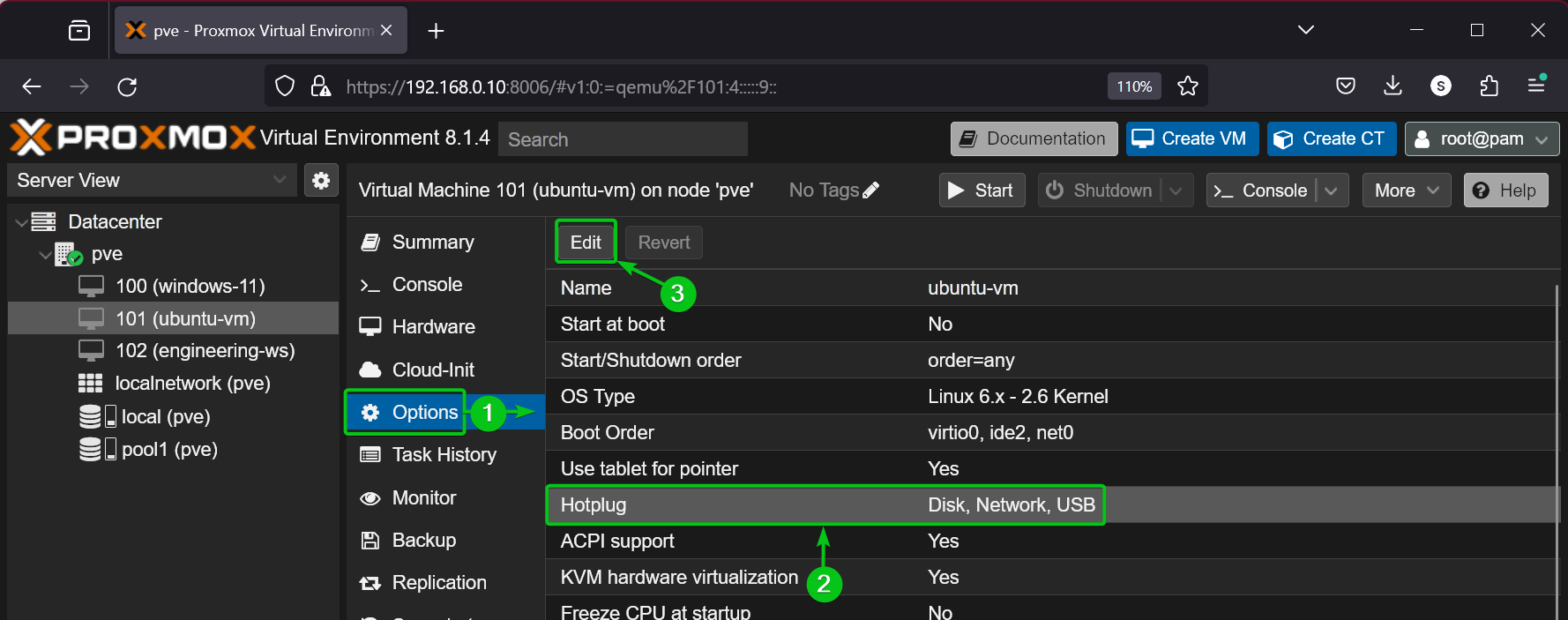
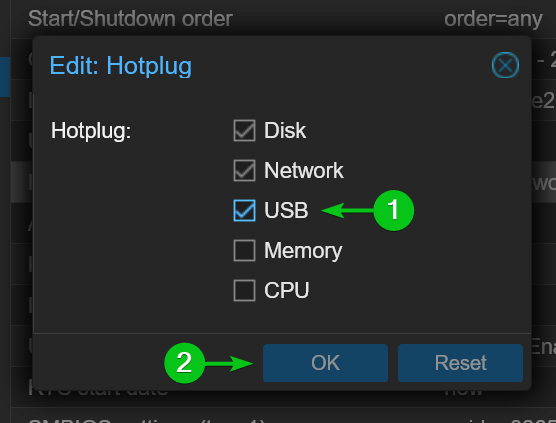
Make sure USB is selected in the Hotplug settings[1]. Once you’re done, click on OK to save the changes[2].
In my case, USB Hotplug is already enabled. So, the OK button is disabled as no changes are made.
Proxmox VE USB Passthrough Methods
You can passthrough your USB devices on Proxmox VE virtual machines in one of two ways:
- Using Vendor/Device ID of the USB device: If you use this method to passthrough a USB device on a Proxmox VE virtual machine, the USB device will be accessible from the VM regardless of the physical USB port (of your Proxmox VE host) you’ve connected the USB device to. You can call this USB Device Passthrough as well.
- Using Host Bus and Port ID of the USB Port the USB Device is Connected to: If you use this method to passthrough a USB device on a Proxmox VE virtual machine, any USB device connected to the same physical USB port of your Proxmox VE host will be accessible from the VM. Unlike Vendor/Device ID USB passthrough, if you connect the same USB device in a different physical USB port of your Proxmox VE host, the device won’t be accessible from the VM. The problem with this method is that you may accidentally connect a wrong USB device on your Proxmox VE VM. The advantage of this method is that you can passthrough one or more physical USB ports of your Proxmox VE host on a Proxmox VE virtual machine and access any USB devices connected to those physical USB ports from the virtual machine without any configuration change. You can call this USB Port Passthrough as well.
Passthrough USB Devices to Proxmox VE Virtual Machines (VMs)
First, insert your desired USB device in any of the USB port of your Proxmox VE host.
To passthrough the USB device to a Proxmox VE virtual machine, navigate to the Hardware section of the Proxmox VE virtual machine[1], and click on Add > USB Device[2].
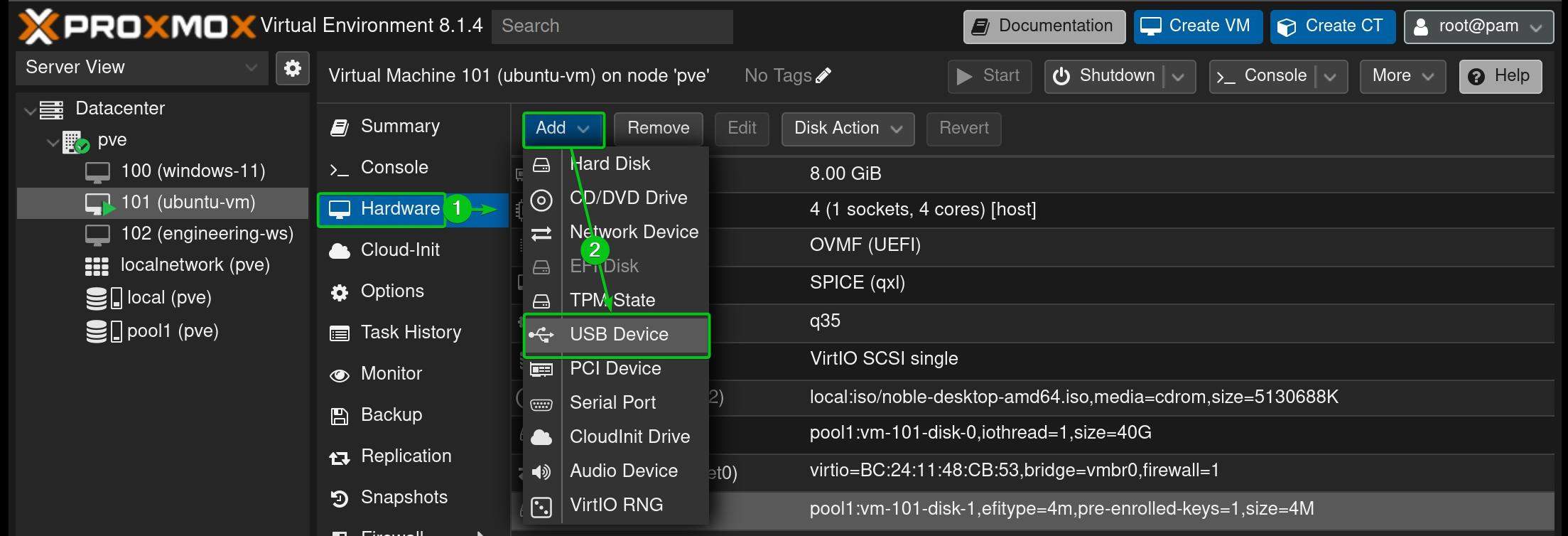
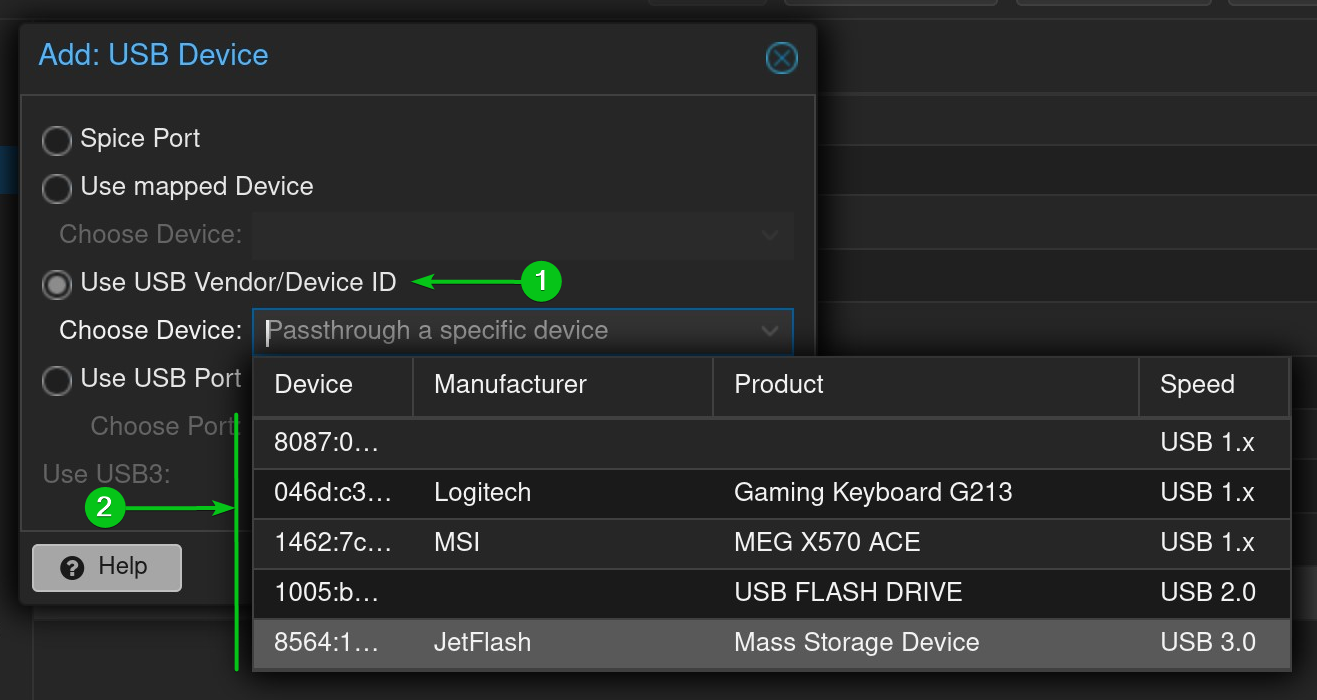
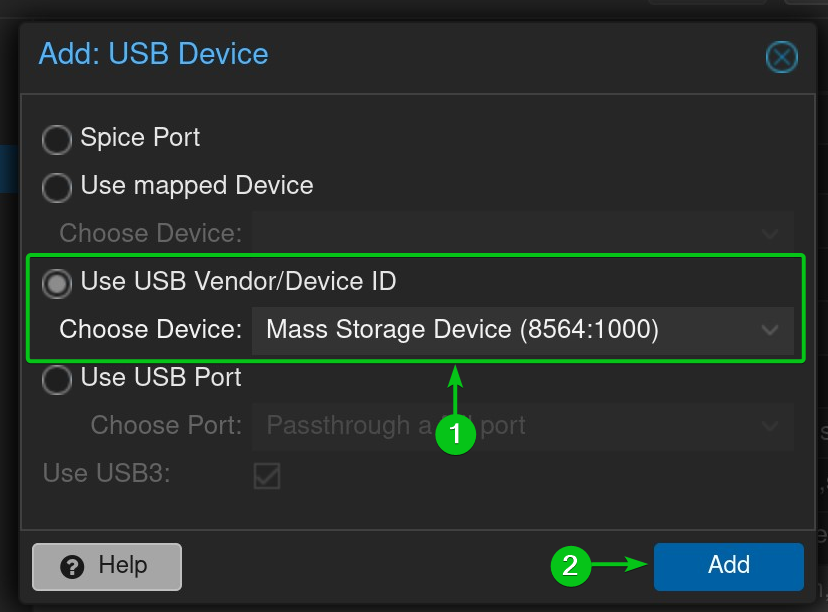
To passthrough a specific USB device to the Proxmox VE virtual machine, select Use USB Vendor/Device ID[1] and select your desired USB device from the dropdown menu[2].
To passthrough a specific physical USB port (of your Proxmox VE host) and the USB device connected to the port on the Proxmox VE virtual machine, select Use USB Port[1] and select your desired USB device from the dropdown menu[2].
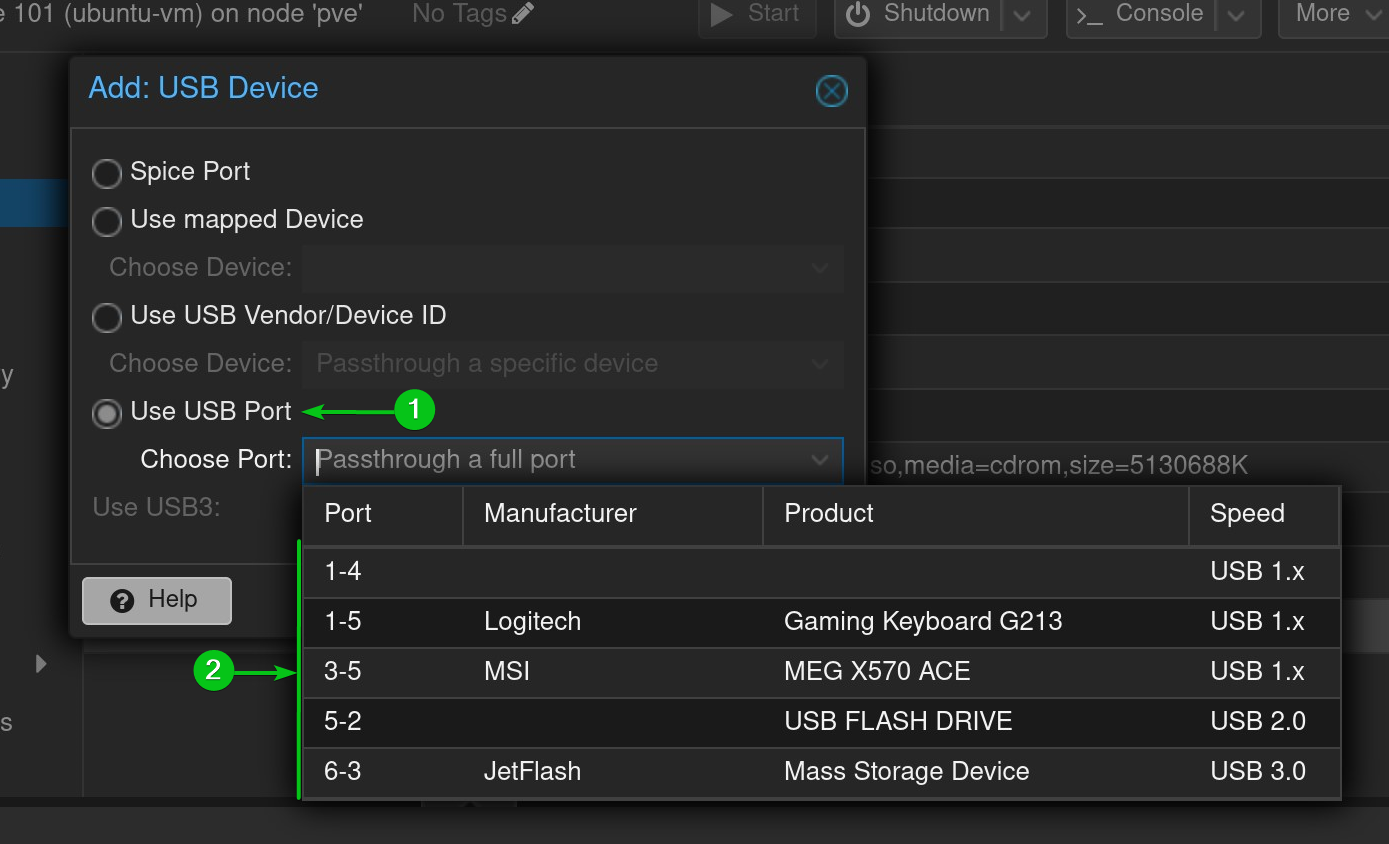
Once you’ve selected your desired USB device/port for passthrough[1], click on Add[2].
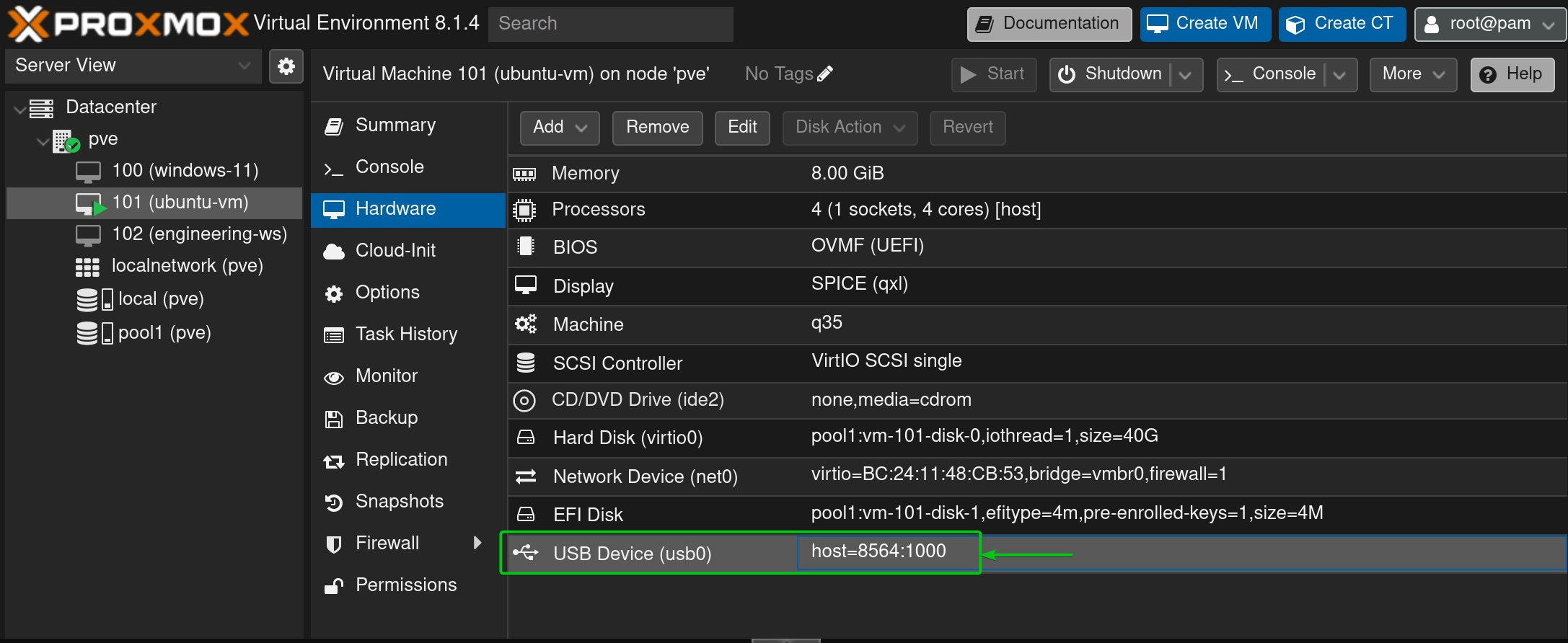
The USB device/port should be added to the Proxmox VE virtual machine.
Accessing the USB Device in the Proxmox VE Virtual Machine (VM)
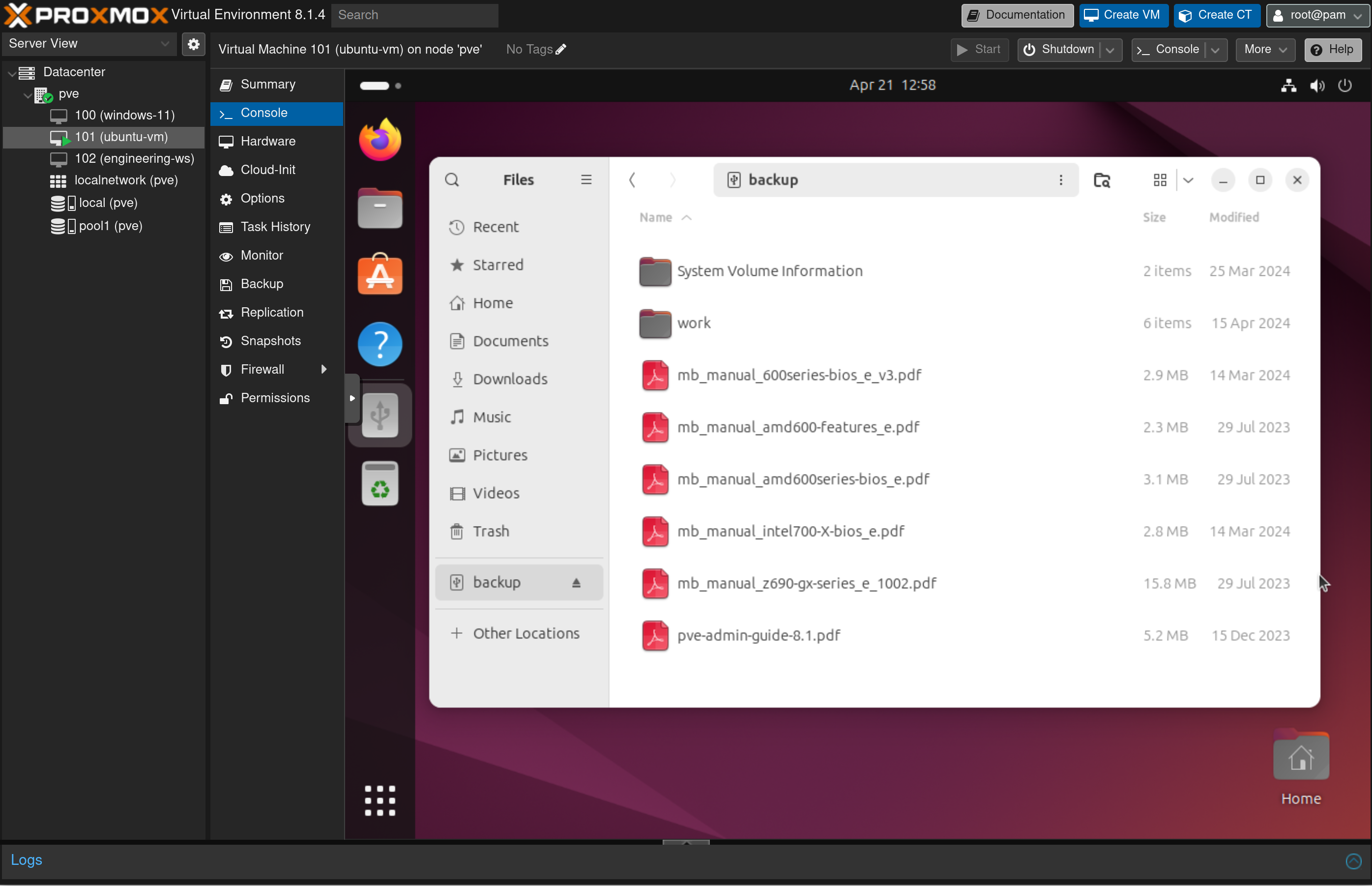
Once you’ve added the USB device/port to the Proxmox VE virtual machine, you should be able to access it from the virtual machine as usual.
Removing the USB Device from the Proxmox VE Virtual Machine (VM)
Once you’re done working with the USB device, you can disconnect it from your Proxmox VE host or remove the USB device from the virtual machine.
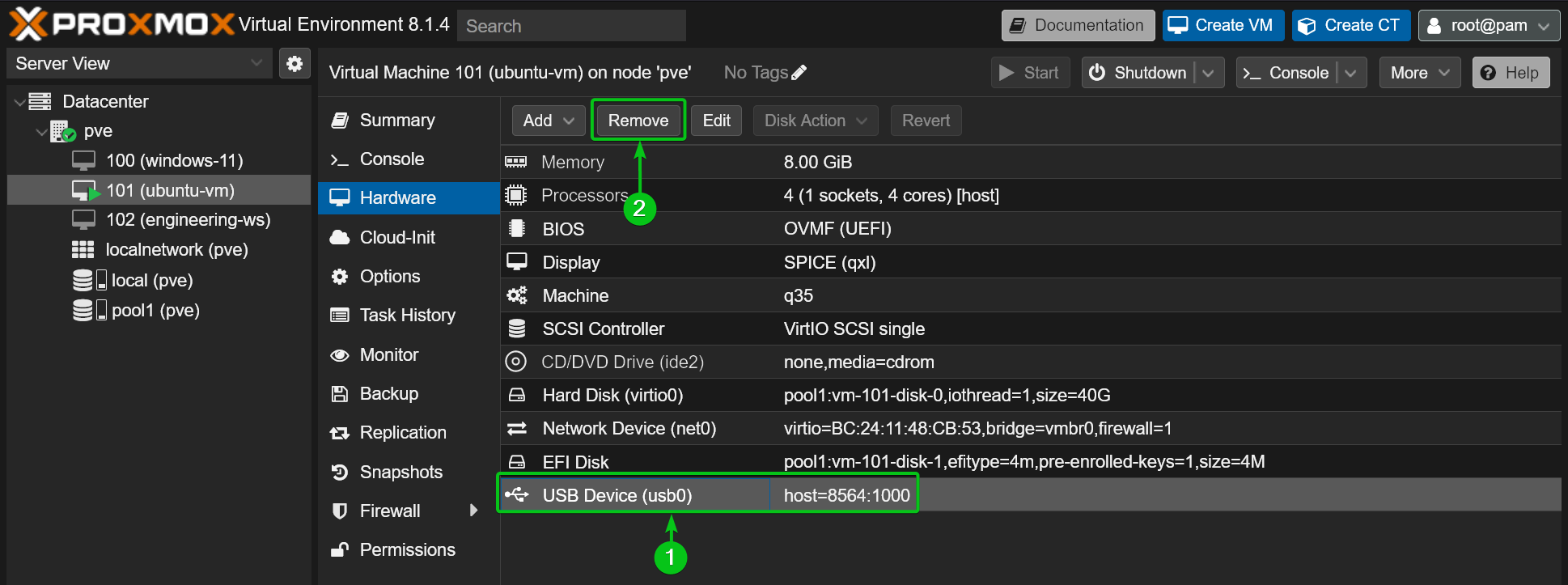
To remove the USB device from the Proxmox VE virtual machine, select the USB device from the Hardware section of the virtual machine[1] and click on Remove[2].
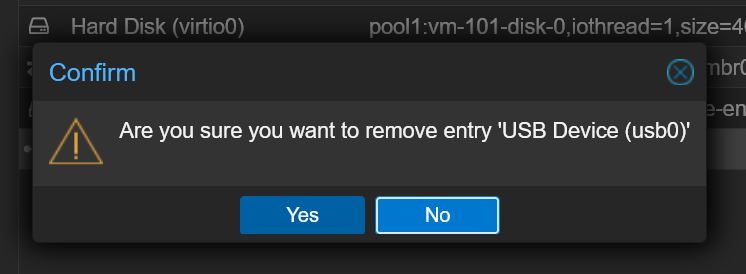
Click on Yes to confirm the action.
The USB device should be removed from the Proxmox VE virtual machine.
Conclusion
In this article, I have shown you how to passthrough a USB device or a physical USB port of your Proxmox VE host on a Proxmox VE virtual machine and access the USB device from the virtual machine. I have also shown you how to remove the USB device/port from the Proxmox VE virtual machine.
References
More...