In a lab environment, lots of new users will be using JupyterHub. The default Authenticator of JupyterHub allows only the Linux system users to log in to JupyterHub. So, if you want to create a new JupyterHub user, you will have to create a new Linux user. Creating new Linux users manually might be a lot of hassle for you. Instead, you can configure JupyterHub to use FirstUseAuthenticator. FirstUseAuthenticator as the name says, automatically creates a new user while logging in to JupyterHub for the first time. After the user is created, the same username and password can be used to log in to JupyterHub.
In this article, I am going to show you how to install the JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator on the JupyterHub Python virtual environment. I am also going to show you how to configure JupyterHub to use the FirstUseAuthenticator.
NOTE: If you don’t have JupyterHub installed on your computer, you can read one of the articles depending on the Linux distribution you’re using:
- How to Install the Latest Version of JupyterHub on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS/ Debian 12/Linux Mint 21
- How to Install the Latest Version of JupyterHub on Fedora 38+/RHEL 9/Rocky Linux 9
Table of Contents:
- Creating a Group for JupyterHub Users
- Installing JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator on the JupyterHub Virtual Environment
- Configuring JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator
- Restarting the JupyterHub Service
- Verifying if JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator is Working
- Creating New JupyterHub Users using JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator
- Conclusion
- References
Creating a Group for JupyterHub Users:
I want to keep all the new JupyterHub users in a Linux group jupyterhub-users for easier management.
You can create a new Linux group jupyterhub-users with the following command:
$ sudo groupadd jupyterhub-users
Installing JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator on the JupyterHub Virtual Environment:
If you’ve followed my JupyterHub Installation Guide to install JupyterHub on your favorite Linux distributions (Debian-based and RPM-based), you can install the JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator on the JupyterHub Python virtual environment with the following command:
$ sudo /opt/jupyterhub/bin/python3 -m pip install jupyterhub-firstuseauthenticator
The JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator should be installed on the JupyterHub virtual environment.
Configuring JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator:
To configure the JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator, open the JupyterHub configuration file jupyterhub_config.py with the nano text editor as follows:
$ sudo nano /opt/jupyterhub/etc/jupyterhub/jupyterhub_config.py
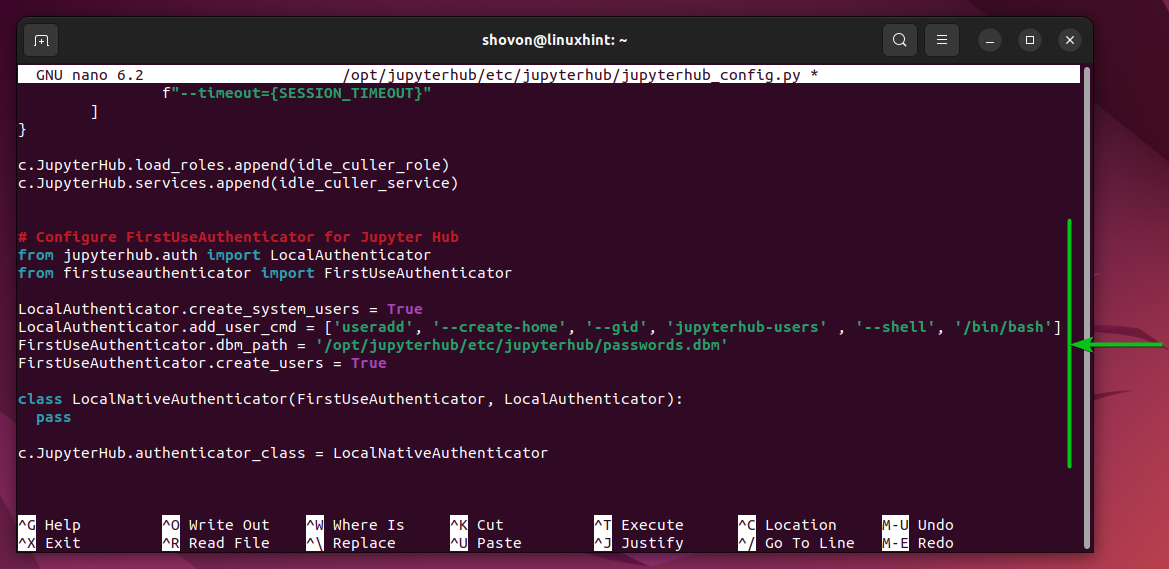
Type in the following lines in the jupyterhub_config.py configuration file.
# Configure FirstUseAuthenticator for Jupyter Hub
from jupyterhub.auth import LocalAuthenticator
from firstuseauthenticator import FirstUseAuthenticator
LocalAuthenticator.create_system_users = True
LocalAuthenticator.add_user_cmd = ['useradd', '--create-home', '--gid', 'jupyterhub_users' , '--shell', '/bin/bash']
FirstUseAuthenticator.dbm_path = '/opt/jupyterhub/etc/jupyterhub/passwords.dbm'
FirstUseAuthenticator.create_users = True
class LocalNativeAuthenticator(FirstUseAuthenticator, LocalAuthenticator):
pass
c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = LocalNativeAuthenticator
Once you’re done, press + X followed by Y and to save the jupyterhub_config.py file.
Restarting the JupyterHub Service:
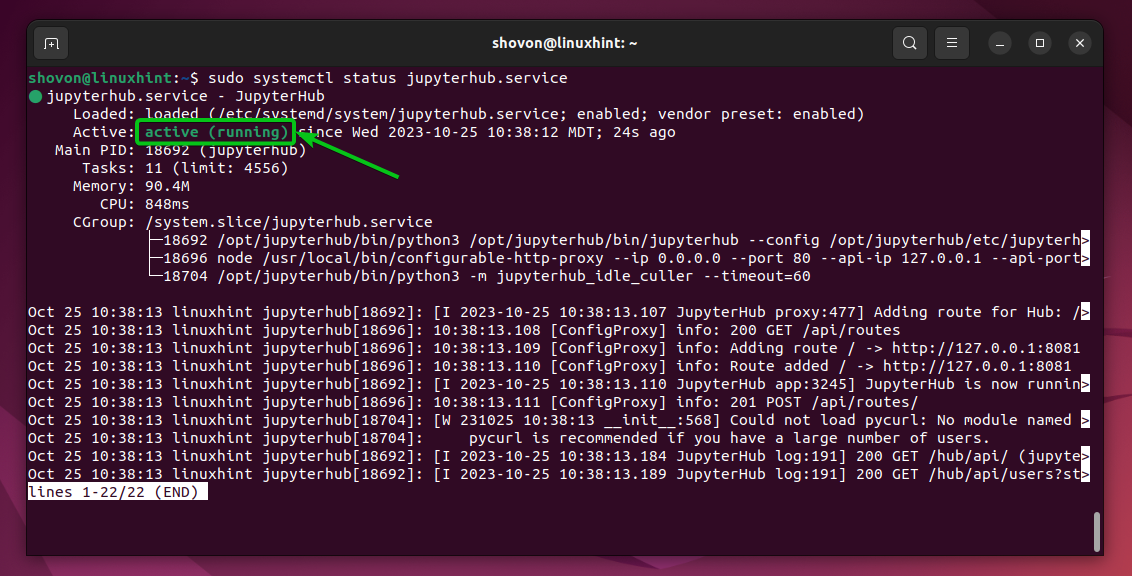
For the changes to take effect, restart the JupyterHub systemd service with the following command:
$ sudo systemctl restart jupyterhub.service
If the JupyterHub configuration file has no errors, the JupyterHub systemd service should run just fine.
Verifying if JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator is Working:
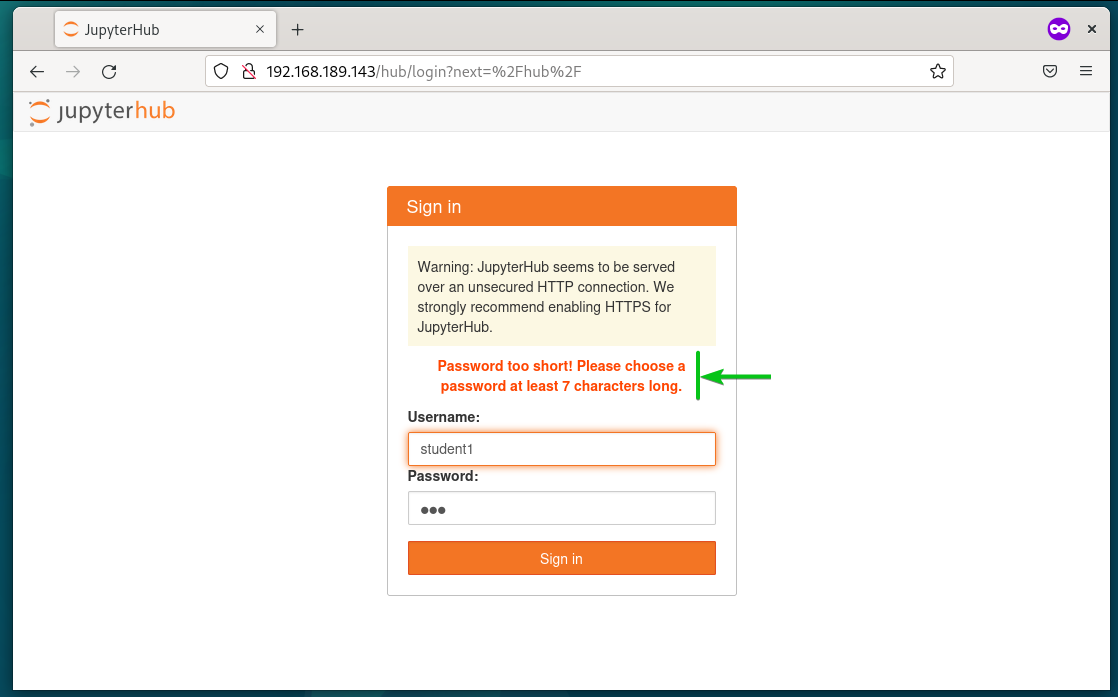
To verify whether the JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator is working, visit JupyterHub from your favorite web browser and try to log in as a random user with a short and easy password like 123, abc, etc.
You should see the marked error message that the password is too short and the password should be at least 7 characters long. It means that the JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator is working just fine.
Creating New JupyterHub Users using JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator:
To create a new JupyterHub user using the FirstUseAuthenticator, visit the JupyterHub login page from a web browser, type in your desired login username and the password that you want to set for the new user, and click on Sign in.
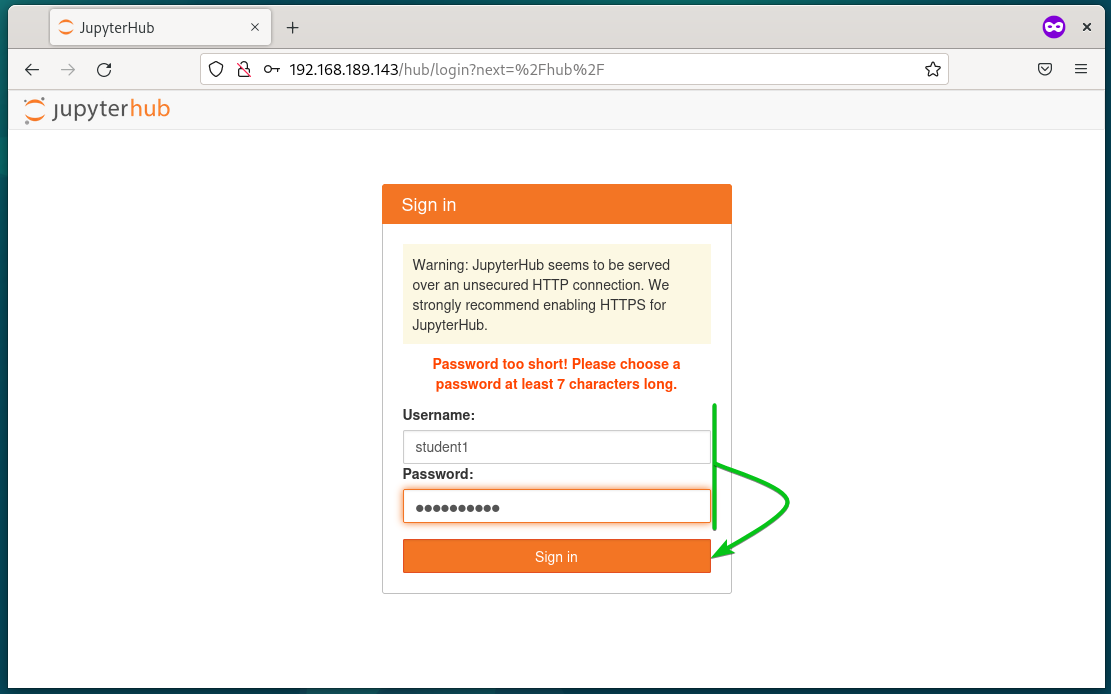
A new JupyterHub user should be created and your desired password should be set for the new user.
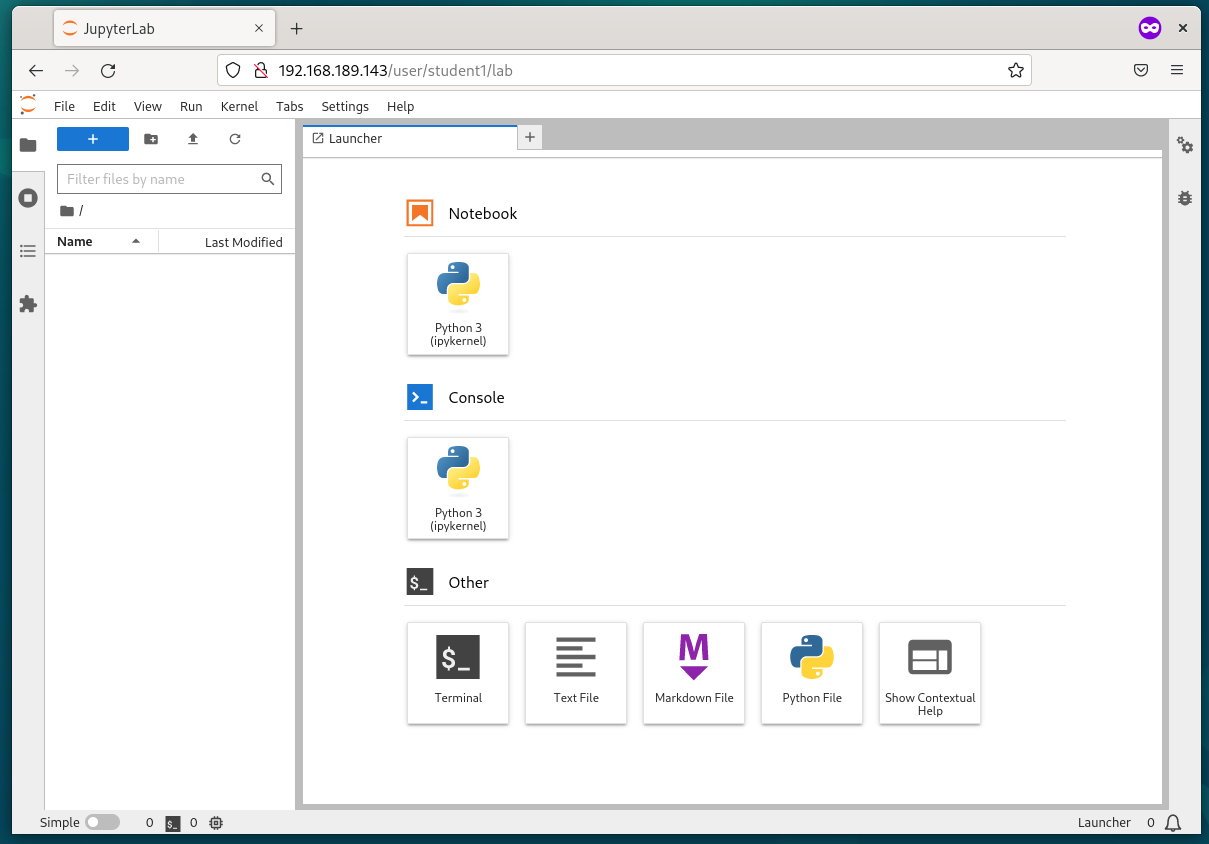
Once the new user is created, the newly created user should be logged into his/her JupyterHub account.
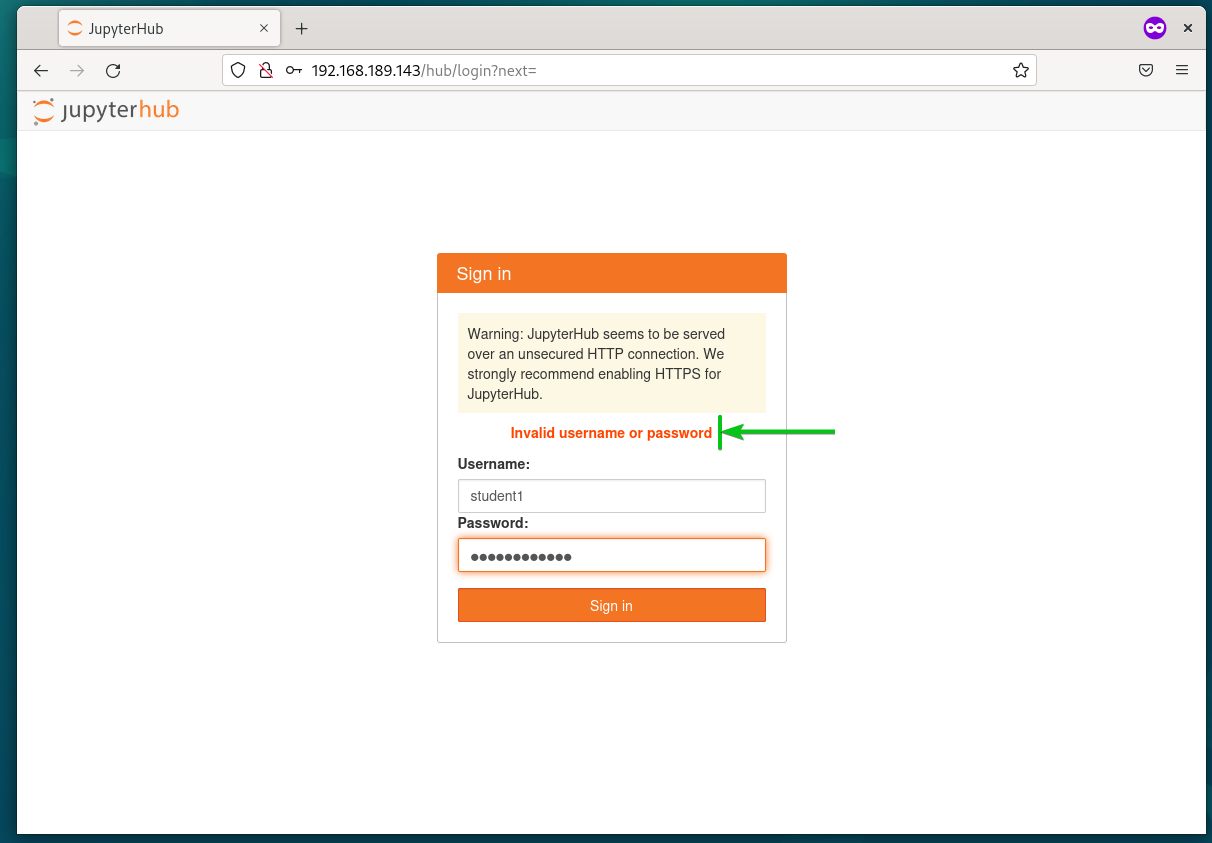
The next time you try to log in as the same user with a different password, you will see the error Invalid username or password. So, once a user is created using the FirstUseAuthenticator, only that user can log in with the same username and password combination. No one else can replace this user account.
Conclusion:
In this article, I have shown you how to install the JupyterHub FirstUseAuthenticator on the JupyterHub Python virtual environment. I have also shown you how to configure JupyterHub to use the FirstUseAuthenticator.
References:
More...