The Node Package Manager (NPM) is a tool that allows developers to install and work with different JavaScript packages efficiently. Installing NPM involves installing Node.js, and this post shares all the insights you need to install NPM.Node.js is a suitable option for anyone looking to have a scalable backend that utilizes JavaScript. Node.js is built on Chrome’s V8 JS engine, and you can easily install it on your Ubuntu 24.04 to start powering your backend functionality in your projects. We will focus on understanding three options for installing NPM on Ubuntu 24.04.
Method 1: Install NPM on Ubuntu 24.04 via APT
You can find the NPM and Node.js from the Ubuntu repository. If you don’t need any specific Node.js version for your project, you can utilize this option to install NPM and Node.js with the below commands.
First, run the update command.
$ sudo apt update
Next, source Node.js from the default repository and install it using the command below.
$ sudo apt install nodejs
At this point, you have Node.js installed, and you can verify the installed version using the command below.
$ node -v

To install NPM, run the following command.
$ sudo apt install npm
Verify that NPM is installed by checking its version.
$ npm --version

We have npm v9 for our case. You can now comfortably start working on your Node.js project, and with NPM installed, you have room to install any dependencies or packages.
That’s the first option of installing NPM and Node.js on Ubuntu 24.04.
Method 2: Install NPM Using NodeSource PPA
When you install the NodeSource package, it will install NPM without you needing to install it separately. This method allows you to install a specific Nodejs package provided you’ve correctly added the PPA by downloading it using wget or curl.
Start by visiting the Nodejs project to see which version you want to install.
Once you decide on the version, retrieve it using curl as in the following command. For our example, we’ve retrieved version 20.x.
$ curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_20.x -o nodesource_setup.sh
The script will get saved in your current directory, and you can verify it using the ls command.
The next step is to run the script, but before that, you can open it with a text editor to confirm that it is safe to execute.
You can then run the script using bash with the following command.
$ sudo bash nodesocurce_setup.sh
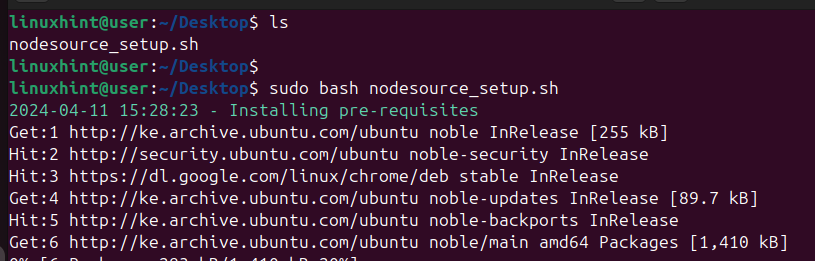
The command will add the NodeSource PPA to your local package, where you can source and install Node.js. When the script completes executing, you will get an output confirming the PPA has been added, and it will display the command you should use to install Node.js.

Note that before installing the Node.js package, if you have already installed it using the previous method, it’s best to uninstall it to avoid running into an error. To do so, use the below command.
$ sudo apt autoremove nodejs npm
To install the Nodejs package, which will also install NPM, run the following command.
$ sudo apt install nodejs
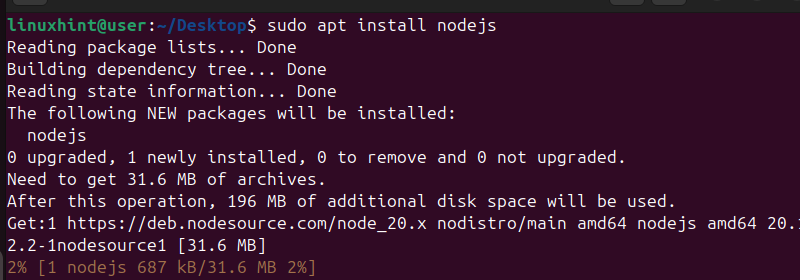
Your system will source the package from the local package where we added the PPA. It will then proceed to install the NodeSource package version that you downloaded.
Once the installation is complete, check its version using the following command.
$ node -v

The output will display the node version you downloaded, which is v20.12.2 for our case. Still, if we check the installed NPM version, you will notice it’s different from what we had earlier.
$ npm --version
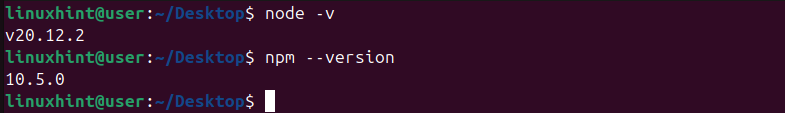
The PPA installed NPM v10.5.0, which is higher than what we installed in method one earlier.
Conclusion
For anyone looking to use NPM and Node.js to power their backend application, this post shares two different methods for seamlessly installing NPM. This allows you to run your Node.js and install packages effectively. You can install NPM from the default Ubuntu 24.04 repository or add its PPA from the Node Source project, which will automatically install NPM alongside Node.js.
More...