With Git, you can comfortably track changes in your repository, revert changes, and more. Moreover, Git makes it easy to maintain your code in Git repositories. Before you can use Git on Ubuntu 24.04, you must know how to install it. Luckily, there are two installation options, and both are detailed in this guide.
Two Methods of Installing Git on Ubuntu 24.04
Installing Git only requires access to a non-root user account and an internet connection. The method to use will depend on your preference. If you want a quick and easy way, installing Git from the Ubuntu repository is recommended. However, this method doesn’t install the latest Git version.
If you want the latest version, you must install Git from its source. This approach involves more steps, but it gets the job done once you know which commands to run.
Method 1: Install Git on Ubuntu 24.04 from Ubuntu Repository
Git is available in the default packages on Ubuntu, and this version is considered more stable despite not being the latest version. Again, this method allows you to install Git using APT with a simple command.
Some packages are installed by default, and in Ubuntu 24.04, you should have Git already installed. Verify this by checking its version.
$ git --version

If Git is not installed in your case, start by updating your package list.
$ sudo apt update
After updating the package index, we can then install Git as follows.
$ sudo apt install git
It’s that simple. Once the process runs and completes, Git will be available on your system, and you can configure it to start using it.
If you want to install the latest Git version, use the following method.
Method 2: Install Git on Ubuntu 24.04 from Source
With the first method, we managed to install Git, but the installed version was not the latest. When you source packages from the default repository, you only access the latest stable version.
However, this doesn’t mean you can’t get the latest Git version. To do so, you must compile Git from the source. Unlike the previous method, this approach takes more time, and you must run different commands to retrieve the package and compile it.
Step 1: Install the Dependencies
For us to source and compile Git, different packages are required, and we can install them using the command below.
$ sudo apt install libz-dev libssl-dev libcurl4-gnutls-dev libexpat1-dev gettext cmake gcc
Those already installed will be skipped during the installation.
Step 2:Create a Temporary Directory
We need a temporary directory to store and compile the retrieved Git files. We’ve named the directory tmp and navigated into it.
$ mkdir tmp
$ cd /tmp

Step 3: Download the Latest Git Version
You can only find the latest Git version from its website. To know which version you should download, visit the Git project website. Once the site loads, locate the latest version. We have v2.44.0 as the latest when writing this post.
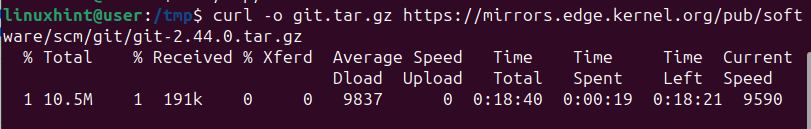
Next, use curl to download the Git tarball with the below command.
$ curl -o git.tar.gz https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/software/scm/git/git-2.44.0.tar.gz
Ensure you replace the command to match the latest version, depending on when you read this post.
Step 4: Unpack the Tarball
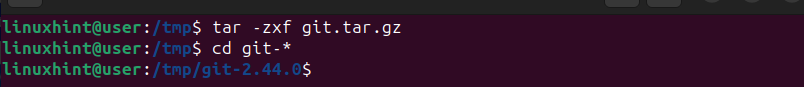
Once you download the Git tarball, we must unpack it using tar. After unpacking, use the cd command to navigate to the Git directory.
$ tar -zxf git.tar.gz
$ cd git-*
Step 5:Compile and Install Git
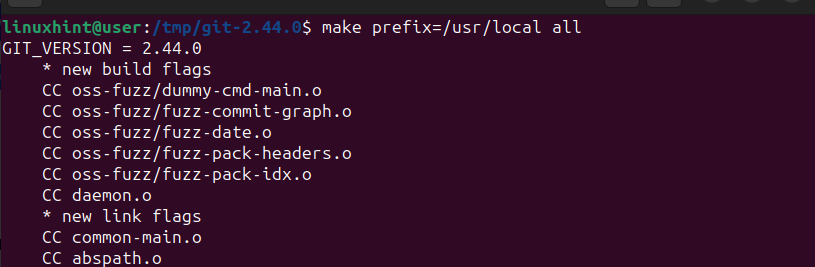
Start by Compiling the Git package using the make command.
$ make prefix=/usr/local all
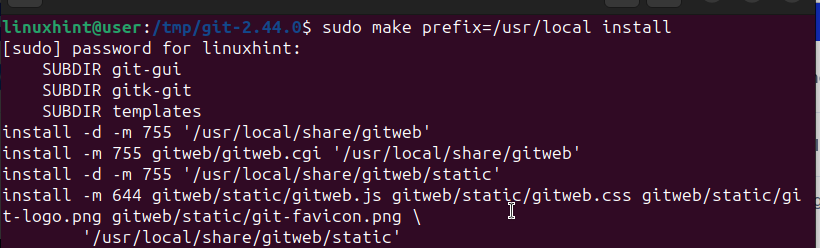
Afterward, install the package by running the command below.
$ sudo make prefix=/usr/local install
Lastly, apply the changes with the command below.
$ source /etc/environment

That’s it. You now have Git installed. Check the version to confirm that we installed the latest one.
$ git --version

We have v 2.44.0, which is what we downloaded earlier.
Configure Git on Ubuntu 24.04
Now that you’ve installed Git, the next recommended step is to configure your username and email. To achieve this, run the below commands and add your username to use when making a commit and the email address.
$ git config --global user.name “your_name"
$ git config --global user.email "your_email"
You can now start using Git to make your commits on your repository.
Conclusion
Git is a widely used version control system, and there are two methods for installing it on Ubuntu 24.04. First, you can install it via APT from your default packages. Alternatively, you can source and compile the Git package to get the latest version. That’s it!
More...