All UNIX-based operating systems, including Linux, follow the structure that “everything is a file.” These systems treat all the regular files, directories, processes, symbolic links, and devices like external hardware as files. You can create, modify, and delete files using the commands or from the File Manager.
Deleting files is essential when you accidentally create multiple files that become unnecessary for the system. So, in this quick blog, we will explain quick ways to delete a file in Linux with no trouble. There are a few methods of deleting the files, so let’s look at them individually with the correct examples.
The rm Command
You can use the rm command to delete the file from the terminal. For example, you want to delete the “filename.txt” located in the Downloads directory, so first run the below command to open the directory in the terminal:
cd ~/Downloads

Then, use the following command:
rm filename.txt
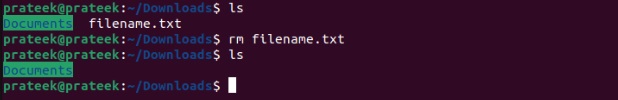
The rm command doesn’t display any output, but you can use the -v option to get the output:
rm -v filename.txt

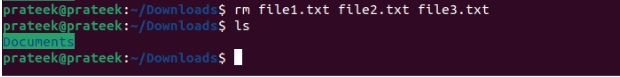
If you want to delete multiple files from the current directory, you can mention all those files in a single rm command. For example, to delete three files– file1.txt, file2.txt, file3.txt, please run the below command:
rm file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt
In case you want to delete all the files with the same extension, then you can run the following command:
rm *.txt
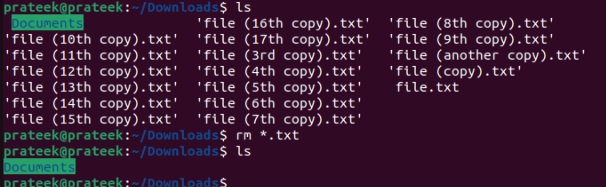
As the above image shows, we have deleted all the .txt files from the Downloads directory. Moreover, you can use multiple extensions in a single command to delete different types of files simultaneously. For example, let’s delete all the files having the .txt and the .sh extensions:
rm -v *.sh *.txt
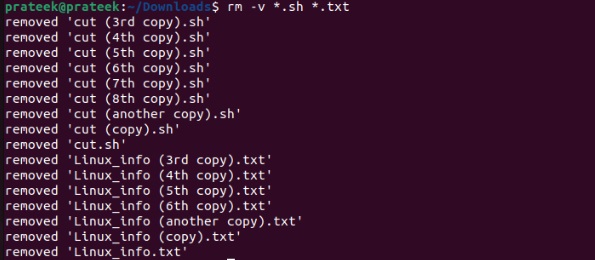
Similarly, you can empty a directory by only adding the * in the rm command:
rm *

Remember, the above command deletes all files except the directories. Hence, if there is a subdirectory, then the terminal will show the following output:

However, you can use the -r option with the rm command to delete the subdirectories. The -r option recursively deletes the directory along with its contents:
rm -r *

In case you want to get the confirmation before deleting the file, please use the -i option.
rm -i *
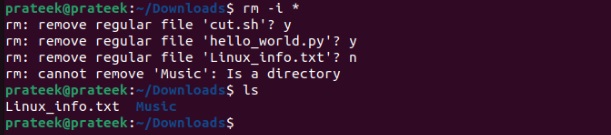
Once you run the command, the system will show a confirmation prompt, so all you have to do is press Y to delete or N to decline it.
From the File Manager
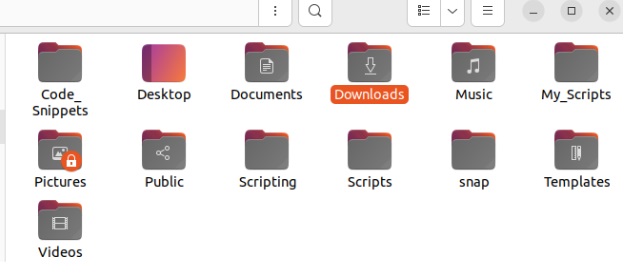
We recommend deleting the file from the File Manager if you are a Linux beginner. So first open the File Manager and locate the directory:
Now select the file and right-click it to get the context menu.
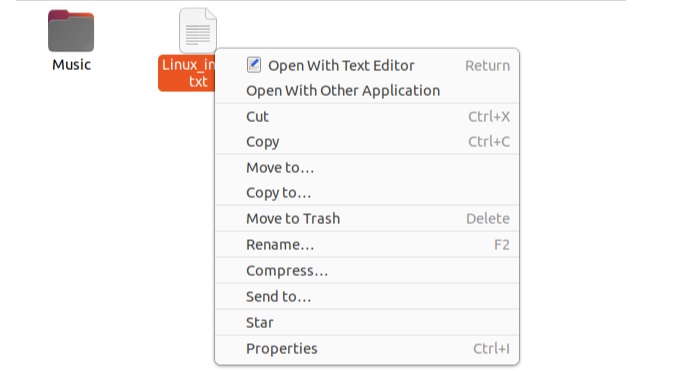
Finally, click on the Move to Trash option or press Delete button.
A Quick Wrap-up
Linux has various commands and methods to delete a file quickly. However, users must know how to delete files to maintain an organized system and minimal storage consumption. This quick tutorial explained two ways of doing so. Initially, we discussed how the rm command works, then explained briefly the step-by-step process of deleting files using the GUI.
More...