Masking a systemd service means the service is disabled and cannot be enabled, even by the system or on manual command. Masking is a stronger form of disabling.
In this guide, I will walk you through how to mask a service on Linux using systemctl, and how to unmask it. Moreover, I will cover key differences between a masked service and a disabled service.
Warning: On Linux, the services are interdependent. Since masking the service disables it and prohibits any activation, therefore use it carefully.
Before going further, let’s first understand the mechanism behind the masked service.
What is a Masked Service
A masked service is a permanently disabled service that prevents it from being enabled by the system or system administrator. System administrators generally use the mask option to deactivate the malfunctioned or conflicting services. However, it is recommended to use this option with caution, as masking a crucial system service may bring hurdles in booting the system.
How to List Masked Services
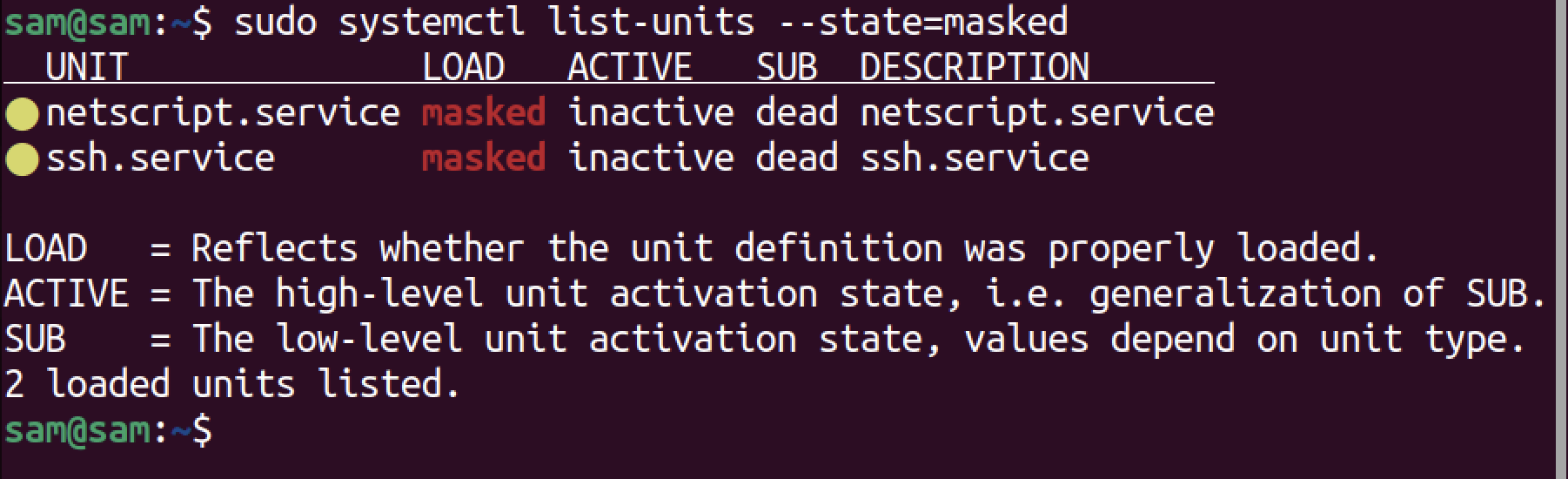
To list masked services on Linux, use the list-units option with the state mentioned masked.
systemctl list-units --state=masked

How to Mask a Service
The systemctl command can be used to mask any service with the mask option. The general syntax of the command is mentioned below.
sudo systemctl mask [Service-Name]
The mask option in the above syntax essentially makes a symbolic link to the service in the /etc/systemd/system.
One or more services can also be mentioned, separated by a space.
Let’s mask the SSH service using the above syntax.
sudo systemctl mask ssh.service

To check the status of a masked service, use the –state= option with systemctl list-units.
If you attempt to start the service, you will receive an output saying that the unit is masked.

Note: You cannot mask a service created in the /etc/systemd/system directory. Because services in this directory are essential for system operations, masking them can harm normal system functionality. However, disabling these services is equivalent to masking them.
How to Mask a Service Temporarily
A service can be masked untill the next boot by using the –runtime option.
sudo systemctl mask [Service-Name] --runtime
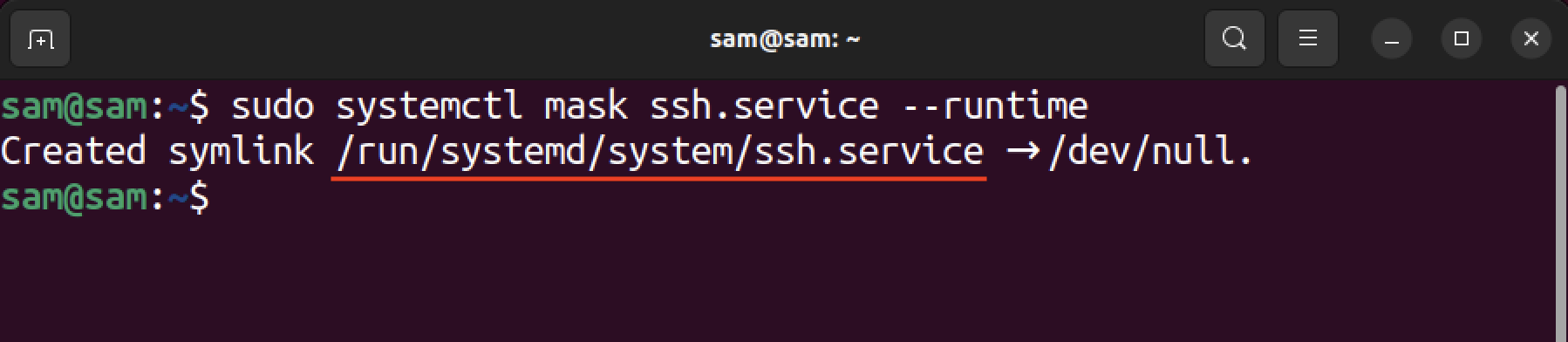
It creates a symbolic link of the service in the /run/systemd/system directory. If the symbolic link of the service is already present in the directory, then the service is designed to be masked temporarily.
How to Unmask a Service
Use the systemctl command with the unmask option to remove the mask restrictions. This command will not accept the path of the service, therefore, only service names are required to be mentioned.
sudo systemctl unmask [Service-Name]
You may need to reboot the system after unmasking the service.
Difference between a Masked Service and a Disabled Service
A disabled service can be enabled and started by the system and on manual commands. However, the masked service cannot be enabled, neither by the system nor by manual interaction.
When a service is made disabled, a symbolic link that is created in the /etc/systemd/system directory is removed, and the service does not activate on boot. But it can be activated by the dependent services.
On the other hand, the masked service is linked to the /dev/null which makes it permanently unusable.
Note that the /dev directory contains the files of the block devices. The /dev/null is a virtual device that removes anything written to it. It is generally used to discard output from stdout and stderr.
Conclusion
If you want to make any service permanently disabled, then use the systemctl mask command. A masked service cannot be enabled even by the system. In this guide, I covered how to mask a service permanently, and temporarily. Moreover, we also mentioned a method to unmask a service and the key differences between a masked and a disabled service.
More...